Not everyone chooses to eat fast food and semi-finished products by their own decision. It is challenging to find fresh produce such as fruits and vegetables in some regions. Statistics show that the United States leads the list of countries regarding the percentage of the population with obesity. Among Americans, about a third of adults are overweight. There are also many overweight people in other countries: for example, one in four people in the world is faced with this problem (Malik et al., 2020). Rampant obesity reflects the decline in the country and highlights that for much of the US population, the quality of life is deteriorating.
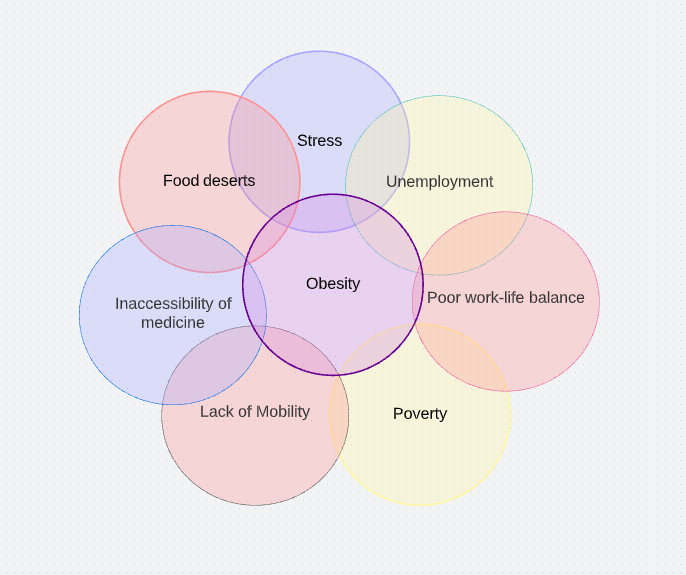
Experts cite a sedentary lifestyle and the wide availability of sugary foods as the main reasons for this trend. There is even a forecast that by 2030 every second inhabitant of the country will be significantly overweight (Kim et al., 2019). It is worth noting that the causes of obesity are more complex and not limited to one or two causes. The Venn diagram below lists the top 7 causes of obesity most commonly diagnosed in the US.
The first reason is the spread and growth of poverty. Due to corporate layoffs, the transfer of American jobs to developing countries, and the economic crash of September 2008, poverty has spread widely throughout the US, where the number of people poor enough to receive food stamps has increased from nearly twenty million at the turn of the century to nearly 50 in 2016 (Palmer & Toth, 2019). Although it is possible to eat healthy food on a small budget, it is tricky, especially when unhealthy processed foods are cheap, ubiquitous, convenient, and easy to get.
As a result, a second reason is singled out – food deserts, or, in other words, regions in which it is difficult to get healthy food, unlike semi-finished products. A food desert store that sells healthy food can be nearly twenty miles away, while a convenience store or cheap food store that sells dangerous food is close to home. Consequently, the infrastructure itself contributes to obesity in some regions.
Factor in time and availability: cheap but unhealthy convenience foods are much faster to prepare and more affordable to buy than even the most common fruits or vegetables. However, processed foods are significantly more expensive for Americans since healthcare costs are among the highest in the US. These factors are compounded by the lack of space and infrastructure for hiking and exercise. In addition, Americans have a relatively high level of stress and mental health problems as the adult population, one of the consequences of which is the consumption of junk food (Kim et al., 2019). It is the poor and oppressed groups of the population, other things being equal, who suffer more from stress and are less able to manage it. Stress also leads to bad habits that contribute to the negative consequences of obesity.
Finally, a high unemployment rate leads to a low level of human mobility. Even if a person has a job, not everyone maintains a balance between personal life and work and either hits workaholism, as they need to feed their families or something else or lead a sedentary lifestyle at work. Against the background of the lack of affordable and accessible medicine in cases where the problem has already appeared, a large percentage of the probability of a problem occurring is created with a tiny percentage of the probability of its solution. The full range of problems is collected in a Venn diagram and displayed in Figure 1.
References
Kim, D., Hou, W., Wang, F., & Arcan, C. (2019). Peer Reviewed: Factors Affecting Obesity and Waist Circumference Among US Adults. Preventing Chronic Disease, 16. Web.
Malik, V. S., Willet, W. C., & Hu, F. B. (2020). Nearly a decade on—trends, risk factors and policy implications in global obesity. Nature Reviews Endocrinology, 16(11), 615-616. Web.
Palmer, M. K., & Toth, P. P. (2019). Trends in lipids, obesity, metabolic syndrome, and diabetes mellitus in the United States: An NHANES analysis (2003‐2004 to 2013‐2014). Obesity, 27(2), 309-314. Web.

