Executive Summary
Analysis of information provides the basic platform for making decisions in an organisation. A large amount of information compels organisations to employ many employees if they (organisations) do not utilise information systems (IS). From the context of Health Authority-Abu Dhabi (HAAD), such an approach introduces ineffectiveness and inefficiencies in decision-making, particularly when decisions from different departments are to be fed into a central platform to arrive at an overall decision to execute a given task. The current paper discusses the role and application of IS/IT system at Health Authority-Abu Dhabi. The goal is to show how it helps in building organisational efficiencies in decision-making.
Introduction
Abu Dhabi Health Authority ensures that people from the emirate have access to quality healthcare. The authority sets strategies for healthcare systems and controls while at the same time monitoring the operations of the healthcare industry organisations. Abu Dhabi Health Services (2015) confirms that the authority also “analyses the health status of the population and performance of the system, and shapes the regulatory framework for the health system” (Para. 1). As a regulator, the authority has the mandates of examining compliance with regulations. It establishes appropriate standards to guide practice. It insists on the urgent need for healthcare organisations to do a benchmark from the evidence-based best practices in healthcare services across the world.
Making vital decisions on all concerns of Health Authority-Abu Dhabi, data collection and processing are incredibly important. The extensiveness of the healthcare sector in Abu Dhabi implies a large amount of data that has to be processed. One of the ways of accomplishing this task is by increasing the number of employees in the organisation.
This step demands the commitment of more organisational resources in reward, training, development, and motivational programmes to increase the productivity of all employees in a bid to ensure rapid processing of data and information. Health Authority-Abu Dhabi (HAAD) can also hire more HRM personnel. This step increases the cost of running the public organisation both in the short-term and long-term. Thus, the organisation finds investing in information systems and information technology important.
Information Systems at Health Authority-Abu Dhabi
Overall Organisational Description
Health Authority-Abu Dhabi (HAAD) takes part in the regulation of healthcare in Abu Dhabi. It shares this role with other organs such as the health ministry, DHA, and EHA. Amid the efforts to introduce different authorities to control and monitor healthcare services, the distribution of responsibilities and powers is not clear to a certain extent. For example, the four elements that comprise the Abu Dhabi health sector, namely DHA, EHA, Health Ministry and HAAD, have had conflicts based on the witnessed overlapping mandates such as licensing and controlling of various medical institutions. HAAD executes its mandates by distributing different organisational functions to different entities, which constitute its organisational structure. HAAD has a functional hierarchical organisational structure. Figure 1 shows the relationship between different elements that make the HAAD organisational structure.
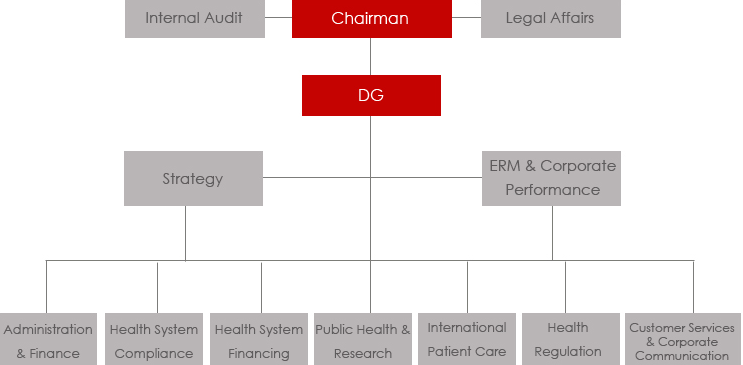
HAAD has the mandate of ensuring the provision of quality healthcare to all Abu Dhabi Emirate citizens. It also takes a proactive role in monitoring the processes of upgrading various hospitals to increase their capacity to handle the entire population’s health-related challenges. This observation means that the size of HAAD covers the entire population of Abu Dhabi. It serves it based on the demand and supply constraints of the healthcare services. As an authority, HAAD is required by law to expand its size to meet the emerging needs of the Abu Dhabi citizens. The organisation targets all citizens from the emirate, health insurance companies, clinics, and other medical facilities.
The IS/IT Department Roles
Different organisations deploy different types of IT tools, infrastructure, and equipment to augment their human efforts or automate operational systems. HAAD deploys an integrated information system. The core of the systems relies on the client-server category of infrastructural architecture. The integrated tools include databases, software for control of various applications and processes, and user interfaces.
Users include HAAD staff members and customers in case of the e-Commutation portal that is integrated with the organisation’s information systems. Since HAAD experiences different changes due to the growing number of service seekers, its IT system is not only flexible, but also highly adaptable to the changing situations. The system is also highly available. This observation means that it is easily accessible for use by different organisational units that are situated in different locations within Abu Dhabi. The system also possesses the capability to simulate various business conditions in an effort to facilitate the process of making vital decisions to enhance future increased effectiveness and efficiency of the authority.
HAAD’s IS/IT system has various tools that enhance its capacity to achieve its integrative roles in making decisions, controlling, and monitoring the organisation’s operations. It has a human resource tool, financial management device, control and monitoring apparatus, and customer management tools among others. It has a workflow, DMS, business intelligence, and portal modules. Transactional databases are used in storing systematic business transactions.
Like in any other organisation that deploys integrated information systems, “the transaction database is used for collecting, updating, processing, and simple presentation of data on certain business processes” (Dusanka & Aleksandar, 2013, p.324). Business intelligence platform deploys data in the HAAD databases to create reports either statistically or dynamically. The IT system uses the TREX technology in indexing various objects to facilitate the display of research results. Workflow encompasses the different logical activities for executing various HAAD business processes without or with minimal intervention of human decision makers.
The IS/IT systems comprise both software and hardware equipment. The software is customised to fit the specific uses and needs of the HAAD. The software is installed in special-purpose computers that have a large processing and storage capacity. To guarantee availability and reliability, buffer solutions are provided. The system is also highly presented since the hardware specifications meet the software requirements as it (software) is specifically customised for use by the organisation’s hardware processing capability.
The IS/IT Role as a Functional Support
The IS/IT has the responsibility of linking various processes and functionalities of different elements of the HAAD. The HAAD serves different insurance companies, clinics, pharmaceutical centres, and even individuals. Therefore, it must enhance efficiency in terms of addressing the concerns of different customers. Fui-Hoon and Lee-Shang (2001) assert that urgency in terms of resolving customer complaints presents a major problem that hinders the success efforts of any organisation. Thus, through IT, HAAD establishes platforms and mechanisms for responding, and ensuring ardent reaction to marketplace demands.
It is for this purpose that HAAD has established an e-Communications portal. Indeed, the increasing number of customers whom HAAD has been attending to has created problems in terms of locating them and/or determining their frequency of service demand. Consequently, without IS/IT systems, making decisions on market targeting may prove problematic. Rapid information processing through IT capabilities ensures that the company deals with the problem of inability to foretell demands such as bed capacity and health insurance needs accurately.
Making target demand forecast decisions in good time aids in determining the appropriate alterations to business practices to serve HAAD service seekers better. Deploying non-computerised information management systems, which are highly dependent on the interaction of human decision-makers (department heads, the CEO, and board members) with segregated information systems that run on different computers, makes it hard to locate past records that involve customer communications. This challenge has led to slowed resolution of customer disputes, a problem that IS/IT systems can address sufficiently.
Without the use of IS/IT systems in effecting the transactions between suppliers and the organisation, holding information in different computers makes it difficult to urgently prepare all documents that relate to specific transactions. For the HAAD, this situation hinders the attainment of strategic plans. Time that is spent in editing or paperwork generation increases the departure of the employee productivity from the ideal situation. IS/IT systems help to resolve this challenge at the HAAD. The systems enhance speedy preparation of documents ranging from invoices, receipts, and customer communications to preparation of service provision plans based on demand. With excessive dependency on human decision-makers and the increased paperwork, it is impossible to expedite service seekers’ needs in a speedy manner.
HAAD assumes the role of developing policies depending on the available data. The IS/IT system supports the process of data collection and analysis. It helps in forecasting human resource needs, training and development, and resource planning and allocation to different areas of operation and utilities. The IS/IT system in the HAAD also produces standardised reports on the general industry performance and bottlenecks.
The high dependency on information systems to provide a platform for making any decision at HAAD suggests that the IT department has a noble responsibility of ensuring high reliability and availability of the system. The department also needs to ensure that the system has no bugs, which may have ramifications of producing misguiding data analysis results and reports. Any person with ill motives on the HAAD may regard IS as an important loophole for attacking the organisation. Therefore, the IT personnel have the responsibility to ensure positive identification of the potential threat to the system emanating from malicious attacks such as cyber attacks.
The IS Role as a Decision-making Support
At HAAD, IS plays a critical role in decision making by enhancing transactional processes and offering decision support modules through an integrated information management system. The decision support system facilitates the making of various decisions based on the analysis of data and statistical projections. Transaction processing system provides the means for collecting data, its storage, modification, or cancelation of transactions (Mureell, 2001).
Such a system is incredibly important since data forms the basis of decision-making at HAAD. All policies developed by the organisation must be backed by the clients’ needs. Therefore, evidence-based approach to making decision is important for HAAD to continue offering reliable services both in the short and long term.
IS/IT systems are incorporated in an organisation to speed up the processes of making decisions based on the collected data. At HAAD, decision support systems create an opportunity for improving the quality of decisions that its leaders make. Through transaction processing system, the HAAD gains an opportunity to permit multiple transactions to occur simultaneously. Data that is collected by the system is held in databases (Fryling, 2010). Later, it is deployed in report production, including billing, reports for scheduling service delivery, wage reports, inventory reports, and check registers.
Transactional and decision support systems are incredibly important in enhancing the decision-making process at HAAD. However, they have some inherent challenges. Maintaining their security constitutes a big issue. For the transactional system, appropriateness of the transactions is overly dependent on the accurateness of the information maintained in the databases. At HAAD, IS/IT is instrumental in the decision-making process by maximising efficiency and effectiveness of arriving at a managerial decision through real-time processing of data.
This way, HAAD leaders and operational personnel produce precise information at any time when required by simply directing the system to do so. For example, HAAD collects data on the performance of hospitals in Abu Dhabi. The data is used to forecast demand gaps. This process involves an intensive data analysis process. The IS/IT integrated system speeds up this process by linking different operational units to the HAAD’s central unit.
Therefore, the organisation stands a chance to not only produce standard reports on demand constraints or supply limitations at the national level, but also on different geographical locations in which HAAD has a legal obligation to control and monitor operations of the healthcare sector. This strategy provides a room for making comparisons to determine differences in healthcare access and utilisation.
Dealing with problems of healthcare crisis requires the possession of accurate and timely information. HAAD’s IS/IT system provides information in such a manner. Indeed, “the use of IS in decision-making during a crisis facilitates an accurate and up-to- information that is required for efficient and effective planning” (Al-Zhrani, 2010, p.1233).
At HAAD, the IS system also provides the necessary information for making decisions such as staff deficiencies, resource allocation, and staff promotion needs. It acts as a tool for increasing the productivity of HAAD by helping to overcome certain deficiencies in human capability such as prolonged working hours at constant speeds. Errors that are associated with limitations in human capability are also eliminated so that the performance of human resource in terms of collection and analyzing accurate and dependable data becomes possible.
Conclusion
Modern organisations in private and public sector need to develop the capacity to process information in a speedy and efficient manner. This situation calls for the design and implementation of IS/IT systems. A major problem that healthcare sector organisations are facing involves developing strategic plans and methodologies for eliminating differences in the capacity to meet the changing workload and the existing human resources capabilities. The HAAD has addressed this challenge by incorporating IS/IT systems in its work processes and management decision-making.
The decision to implement an integrated information processing systems arose from the recognition of the fact that when organisations’ clientele increase, a large amount of data has to be processed to ensure a timely fulfilment of the needs of all service seekers and to execute planning processes of the HAAD. Health Authority-Abu Dhabi’s IS/IT systems has tools such as DMS, transactional databases, human resource management, and tools for managing service seekers’ relationships among other modules that ensure real-time data processing and report production to augment human decision-making processes.
Reference List
Abu Dhabi Health Services. (2015). About the Health Authority-Abu Dhabi. Web.
Al-Zhrani, S. (2010). Management Information Systems Role in Decision Making During Crises: Case Study. Journal of Computer Science, 6(11), 1230-1234.
Dusanka, L., & Aleksandar, K. (2013). The Impacts of MIS on Business Decision Making. TEM Journal, 2(4), 323-326.
Fryling, M. (2010). Estimating the impact of enterprise resource planning project management decisions on post-implementation maintenance costs: a case study using simulation modelling. Enterprise Information Systems, 4(4), 391–421.
Fui-Hoon, F., & Lee-Shang, J. (2001).Critical Factors for Successful Implementation of Enterprise Systems. Business Process Management Journal, 7(3), 285-296.
Health Authority. (2015). About health authority-Abu Dhabi. Web.
Mureell, S. (2001). E–Business and ERP: Rapid Implementation and Project Planning. New York, NY: John Wiley and Sons, Inc.
