Background
The shortage of registered nurses (RNs) continues to affect the United States health care system and medical institutions. The nursing shortage entails intertwined negative consequences for the delivery of medical aid and society as a whole. Health care services are aggravating due to the imbalance between supply and demand for medical personnel, inefficient medical aid, and irrational use of the healthcare workforce. Moreover, there is a growing concern that the significant mismatch between the demand for RNs and the size of the RN workforce will affect the delivery of high-quality healthcare services to the public worldwide.
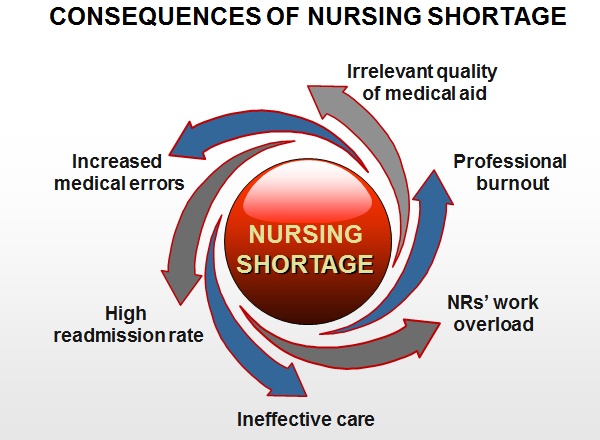
Recent research studies have projected that the need for RNs is going to increase due to the growing rates of ageing population associated with increased life expectancy, low production capacity of nursing schools, a decline in the nursing academia, and turnover trends specific to all medical institutions (American Nurses Association, 2014; Health Resources and Services Administration, 2016). The significance and magnitude of the issue of nursing shortage predetermined research initiation.
Purpose
The purpose of this research was to explore and assess the impacts of the current nursing shortage on health care in the United States.
Methods
In order to synthesize reliable evidence and statistical data pertaining to the current nursing shortage and its influences on health care provision, the mixed-methods systematic review was conducted. The research process entailed the synthesis of “a variety of quantitative, qualitative, and mixed-methods studies” (Burns & Grove, 2014, p. 23). Multiple evidence-based publications and reliable sources were utilized to collect and synthesize information congruent with the purpose, including scholarly research from reputable healthcare organizations, publications of state agencies, peer- reviewed articles, and monographs.
Given the cause-and-effect relationships between factors contributing to nursing shortage and its consequences for the health care system, the determinants of the issue were also considered.
Results
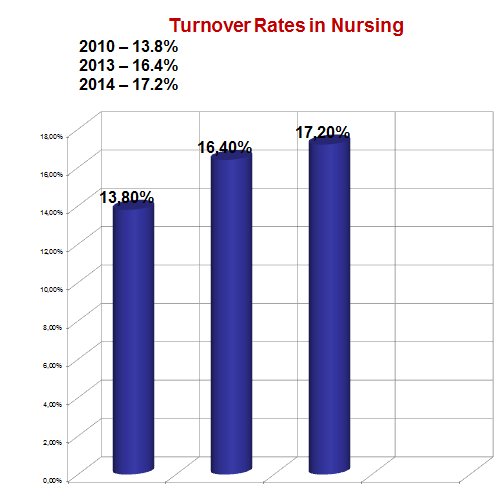
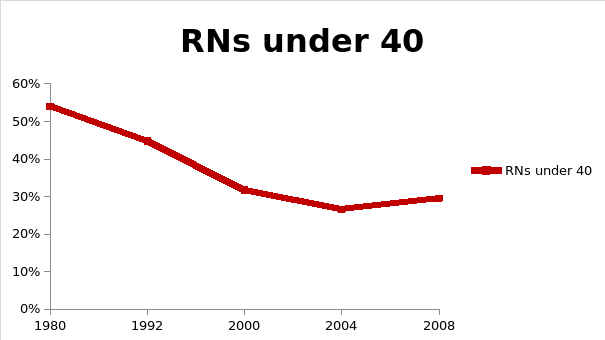
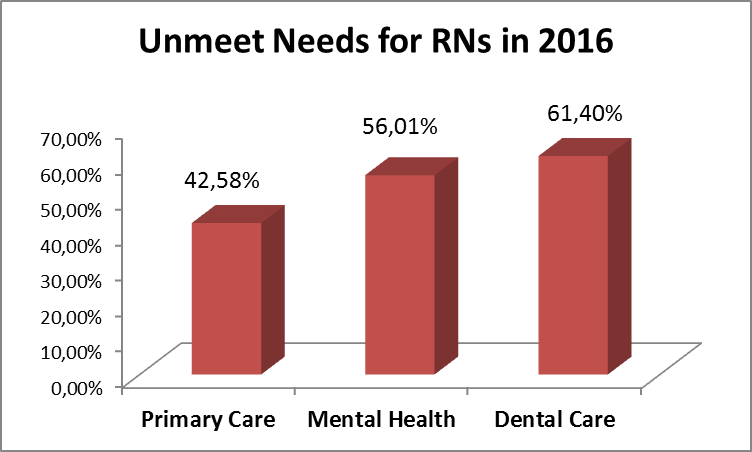
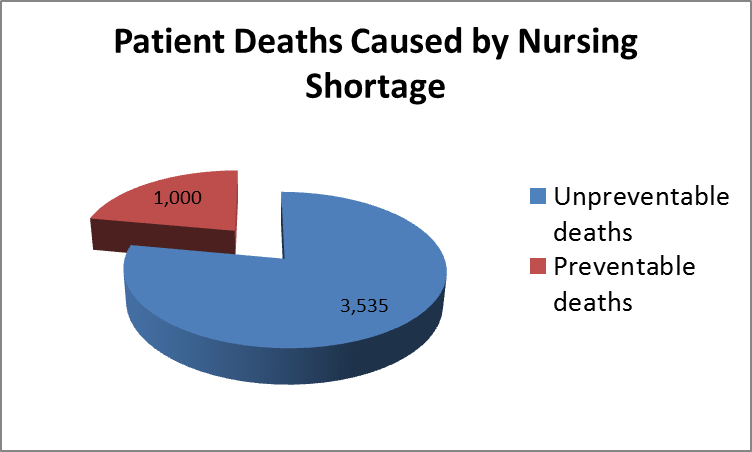
Conclusion
Findings obtained from the mixed-methods systematic review testify to continuous patterns of the nursing shortage in the United States. Despite the initiatives implemented to deal with this problem, current rates of patients’ preventable deaths testify to their insufficiency.
The provision of health care should be in line with changes in the medical paradigm, be cost-effective and affordable, and guarantee high-quality medical aid for all demographics worldwide. This research indicates that the nursing shortage in the United States has significantly influenced the quality of medical aid delivered to the U.S. populations. The expansion of the capacity of nursing schools could rejuvenate the health care workforce. The implementation of evidence-based practices within nursing will retain nurses in their professional areas and increase the effectiveness of RNs’ performance and thus, avert shortages of nurses in the future. Further quantitative research is needed to provide a deeper insight into the background and consequences of the nursing shortage in order to eradicate this issue.
References
American Association of Colleges of Nursing. (2014). Nursing shortage. Web.
American Nurses Association. (2014). The nursing workforce 2014: Growth, salaries, education, demographics & trends. Web.
Burns, N., & Grove, S. (2014). Understanding nursing research. Building an evidence-based practice (6th ed.). Maryland Heights, MO: Elsevier.
Littlejohn, L., Campbell, J., Collins-McNeil, J., & Khayile, T. (2012). Nursing shortage: A comparative analysis. International Journal of Nursing, 1(1), 22-27.
U.S. Health Resources and Services Administration. (2016). Designated health professional shortage area statistics. Web.
