Introduction
Hypertension is a complex medical condition with elevated blood pressure, and the heart has to beat harder to pump blood to all body parts. Human blood is carried to all body parts using the arteries for functioning. As the blood pushes against the arterial walls, pressure is created. When the pressure rises and builds up, the heart has to pump harder for the blood to reach the body parts. The impact of the disease increases the risk for brain and kidney disease hence being one of the most significant causes of premature deaths worldwide. One in every four men and one in every woman are affected globally (Ferdinand et al., 2020). Notably, the health condition is primarily felt in the lower and middle-income economies. The selected population for hypertension analysis is the adults in the USA. Nearly half of American adults suffer from hypertension, and an antidote must be found to improve the people’s risk factors (Rippe, 2019). Leadership and policy changes are essential to understanding and eradicating health conditions.
Reasons for Selecting the Problem
The study was selected because of its impact on quality of life. Over 46% of the people suffering from hypertension are unaware of their condition (Ferdinand et al., 2020). Further, the condition puts people’s lives at risk because it increases vulnerability to stroke, heart attack, heart failure, and other complications. Another important reason hypertension was selected is that the risk factors are prevalent in society (Fowler et al., 2021). The risk factors include age, family history, race, obesity, lack of physical exercise, alcohol uptake and poor balance diet. The risk factors increase the disease’s prevalence, jeopardizing the quality of life.
Relevance of the Problem
Hypertension is relevant not only for patients and their families but also for the general public. When healthcare practitioners get adequate knowledge of the disease, they are likely to prevent it further. Understanding the condition is, therefore, relevant as it helps a person take the necessary precautionary measures (Ferdinand et al., 2020). Society will likely lead a better life as they understand the disease and work towards avoiding the risk factors.
Proposed Intervention
Hypertension awareness and healthcare promotion through posters is the proposed intervention. Hypertension intervention is attained when the risk factors are understood and eliminated. Although the condition may be caused by heredity, lifestyle changes are the antidote to attaining a healthier life. All the risk factors may be avoided when people decide to adjust their lifestyle as a society. Community training on lifestyle changes is the antidote to making people safe from the disease (Fowler et al., 2021). People must be taught and encouraged to eat a balanced diet, have constant and efficient physical exercise, have a therapeutic regimen, and avoid smoking and too much alcohol intake. Healthcare promotion programs help people to understand the risk factors and avoid them for a quality life in the discourse.
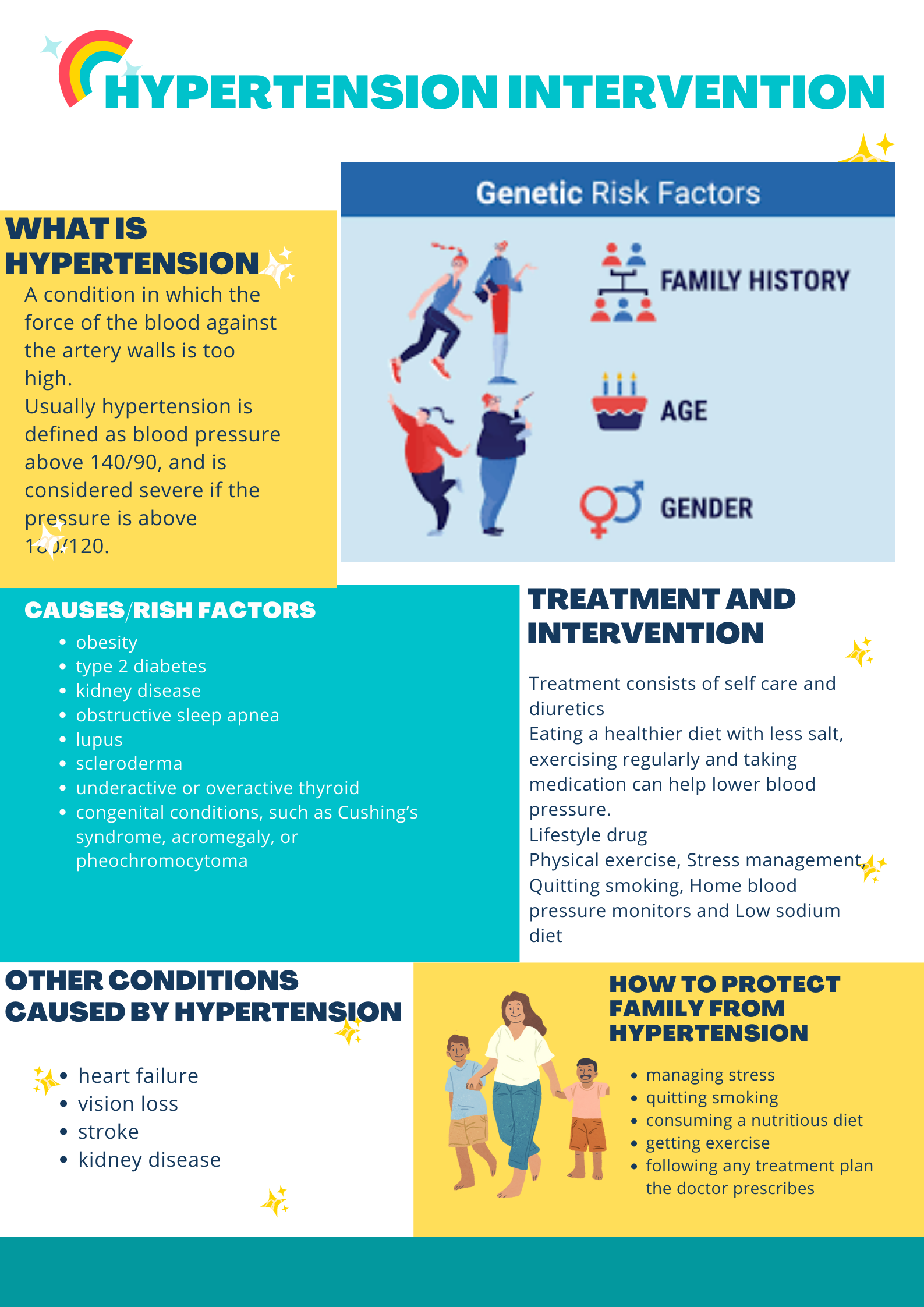
Figure q above depicts a professional poster that serve as an intervention to help people understand the problem and device ways of overcoming it. The proposed intervention will improve the quality of life because as people change their lifestyles, they tend to live healthier lives. Further, patient safety is enhanced because all the risk factors are avoided, and the healthcare system’s cost is lowered. Changing lifestyles ensures they do not use excessive funds for hospital bills, and their overall quality of life will improve.
Role of Technology, Care Coordination and Community Resources
Healthcare promotion through training requires a holistic approach to educating everyone in the community about the healthcare changes. Technology plays a significant role as it will be used as the media for communication where patients learn about the disease and issue their feedback. Care coordination through the formation of multidisciplinary teams to solve the challenges affecting the people in the discourse (Fowler et al., 2021). Community resources such as social halls may be used for the training. Therefore, primary care providers must partner with society to make the awareness successful in offering better results.
Role of Nursing Ethics in Developing Hypertension Intervention
Hypertension affects people worldwide, and the effectiveness of the intervention is determined by the ethics applied. If people are treated with discrimination, the efforts will be jeopardized, and the disease will not be prevented in the long run. Ethics in the intervention is achieved when the information issued is accurate and has autonomy (Heinen et al., 2019). Further, the principles of ethics which strengthen the intervention are accountability, justice, and non-maleficence.
Role of Leadership and Change Management in Addressing Hypertension
Hypertension has affected people globally, and change management is critical to bring relevant changes in people’s lives. As lifestyle changes in developing countries increase the risk factors for hypertension, leadership is critical in maintaining a healthy lifestyle and positive changes in people’s lives (Nieuwboer et al., 2019). Lifestyle modification can only be achieved through positive leadership. Nurses play a significant role in primary health care, and effective leadership assigns exceptional nurses roles to ensure they have achieved better outcomes in the discourse.
Board Nursing Practice Standards Supporting the Intervention
Board nursing practices are critical principles supported by the federal or state government to enhance uniformity when handling healthcare challenges. Nursing board practices for effectiveness support the intervention. The fundamental standards supporting the intervention are medication safety, patient identification and prevention and control of healthcare. The principle of prevention is practiced because when people are educated on hypertension risk factors, they will avoid them, improving the quality of life and lowering the disease’s prevalence (Koutoukidis & Stainton, 2020). The critical guide representing the work requires prioritizing prevention to lower hypertension prevalence.
Effectiveness of the Standards through Research
The healthcare standards set at the federal and state level are essential in improving the quality of life. When the standards are followed, the region’s quality of life will likely improve. For example, when a standard instructs the primary care nursing home to focus on preventive medicine, it will significantly impact the state of health. Research by Nieuwboer et al. (2019) inferred that organizations investing in preventive care would likely improve outcomes in the long run. Abiding by the standards is, therefore, the prerequisite for the quality of health.
Leadership and Change Management Strategies
Prioritizing people’s health is the only strategy used to manage societal change and ensure people work to alter their lifestyles to be safe from hypertension. Establishing a clear vision is a strategy that helps healthcare and community management to eradicate the healthcare challenge (Rippe, 2019). As the leaders train people on the dangers associated with the disease, having a clear goal of eliminating hypertension risk factors is critical for improving health in society (Ferdinand et al., 2020). Ensuring a two-way communication system is vital for collecting feedback, adjusting current lifestyles, and adopting new ones that increase hypertension risk factors.
Strategies for Communicating and Collaborating With the Patient
The effectiveness of the training intervention can only be achieved when communication strategies lead to the complete transfer of information. Some of the strategies to ensure better communication is ensuring there is a multidisciplinary approach for all people to learn regardless of their cultural orientation (Ferdinand et al., 2020). The outcomes will likely be positive when the selected language is aligned with the audience’s culture.
The best practice for effective communication in the healthcare domain includes preliminary training on listening to make people active listeners before being taught the basics of hypertension and how to prevent it. Further, the communication must be designed in a way that is concise, clear, and presented with the highest level of courtesy for it to be understood and appreciated by the audience (Ferdinand et al., 2020). Once the population is aware and takes part in the strategy, they are likely to adjust their lifestyles to achieve a healthier outcome.
Benefits of Gathering the Populations Input To Improve Care
The health concern affects the elderly, who believe they have the right to make decisions affecting their lives. Formulating strategies without the population’s input may appear as imposing rules on independent-minded people. Consequently, they may not abide by the required changes in lifestyle. However, collecting the population’s view on the better ways of avoiding the risk factors is likely to improve efficiency because people are likely to claim ownership of their ideas, making it possible to get better results (Heinen et al., 2019). If a person’s input is included in the medical framework or behavioral change, they will be willing to offer their services.
Conclusion
Hypertension is a complex health condition that jeopardizes people’s quality of life. It affects almost half the global population, and some people are unaware. The health condition is dangerous as it is the prerequisite for other conditions, such as kidney and brain damage, leading to premature death. The risk factors are associated with lifestyle and genetics and require candid advice on avoiding the risk factors. Training and healthcare promotion to alter lifestyle is the antidote to tackling the situation.
References
Ferdinand, D. P., Nedunchezhian, S., & Ferdinand, K. C. (2020). Hypertension in African Americans: advances in community outreach and public health approaches. Progress in cardiovascular diseases, 63(1), 40-45. Web.
Fowler, K. R., Robbins, L. K., & Lucero, A. (2021). Nurse manager communication and outcomes for nursing: An integrative review. Journal of nursing management, 29(6), 1486–1495. Web.
Heinen, M., van Oostveen, C., Peters, J., Vermeulen, H., & Huis, A. (2019). An integrative review of leadership competencies and attributes in advanced nursing practice. Journal of advanced nursing, 75(11), 2378-2392. Web.
Koutoukidis, G., & Stainton, K. (Eds.). (2020). Tabbner’s Nursing Care: theory and practice. Elsevier Health Sciences.
Nieuwboer, M. S., van der Sande, R., van der Marck, M. A., Olde Rikkert, M. G., & Perry, M. (2019). Clinical leadership and integrated primary care: a systematic literature review. European Journal of General Practice, 25(1), 7-18. Web.
Rippe, J. M. (2019). Lifestyle strategies for risk factor reduction, prevention, and treatment of cardiovascular disease. American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine, 13(2), 204–212. Web.

