Health and finance have always been strongly related to each other. This happens because health depends on finance and any other sphere of public life. After all, finance is required for maintaining the performance of healthcare services. Moreover, finance affects the health policy and, thus, the level of quality of health services. Since health is included in the state sector of the economy, this relation between health policy and finance is not likely to change in the nearest future. Governmental control predetermines the possible ways of the development of health policy.
There is a scheme of the relationship between health policy and finance below. This scheme is build based on the structure of governmental interactions and communications between different institutions. Moreover, it reflects the purposes and functions of health policy along with the goals of fiscal policy. Therefore, Figure 1 presents an overview of the mechanism that manages the interactions between finance and health policy so that the goals of both involved parties are possible to achieve.
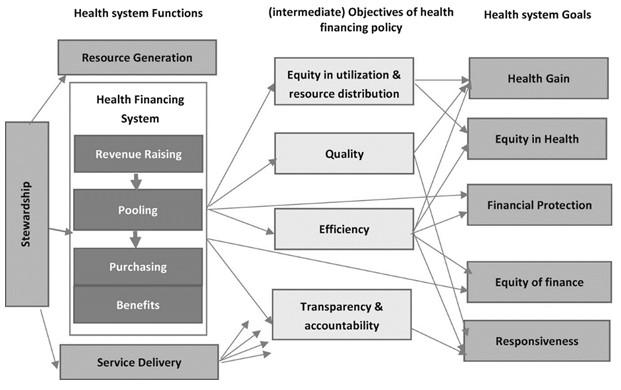
The diagram shows that there are relations between many parts of finance and health services. Most importantly, it represents how the functions of medicine are interlaced with the goals of the finance system. More specifically, some of the goals of finance are included in the health financing system. Health policy and finance united can be referred to as healthcare financing, a new phenomenon. Healthcare financing adheres to managing funds for medical resources needed for providing the primary function of medical care – contributing to people’s wellbeing (“The fundamentals of healthcare financing,” n. d.). In other words, it is needed for making the system of medical services work. Any health policy cannot exist without proper funding, and any alterations should be supported by necessary and relevant finance-related measures and decisions.
Therefore, the health financing system contributes to achieving the goals of finance in general, such as quality of services and performance efficiency. The transparency and accountability of a medical organization are dependent on the service delivery policy. To be more exact, service delivery policy predetermines the financial performance because the service delivery quality and the consequent growth or decrease in the number of clients affect financial indicators directly. Furthermore, the objectives of finance are fundamental for formulating the goals of the health system and health policy as its instrument (Cylus et al., 2018). For example, the need for maintaining financial efficiency and quality, which characterize the success of a business, is reflected in health system goals, such as equity of finance, financial protection, and responsiveness. In addition, health gain as one of health policy goals depends on the mentioned above elements of finance objectives.
Considering the examples of the interconnection which is described above, they are the following:
- Getting permission to buy new equipment for a state clinic requires an agreement from a financial director because the amount of money needed for the changes should be calculated and assessed.
- The state can provide some complex operations, which means the financial department should always be ready to provide the management with the information on the necessary amounts of funding in each period.
Thus, all aspects of health policy depend on finance due to the necessity to fund specific changes or maintenance of some services. The goals of finance and health policy are also connected and laced together, creating a whole system of purposes for both systems at the same time. Finance is one of the most widespread spheres, meaning that it cannot be avoided in public life.
References
The fundamentals of healthcare financing. (n. d.). Cleargage.
Cylus, J., Permanand, G., & Smith, P. C. (2018). Making the economic case for investing in health systems: What evidence is that health systems advance economic and fiscal objectives? Health Systems for Prosperity and Solidarity.

