Introduction
The liver can be said to be a reddish brown organ which weighs approximately 1.4 to 1.6 kg. In addition to these it is soft and triangular which makes it a very vital internal organ. This important organ is located right below the diaphragm where it overlies the gall bladder. The hepatic artery and portal vein are the blood vessels that connect to the liver (Worman 12).
These blood vessels are in charge of supplying blood from the aorta and bringing in digested food. Both of these veins provide dual blood supply to the liver. On the other hand the hepatic portal vein supplies blood that has been drained from other organs. The other supply that remains is accounted for by the hepatic arteries. They are also responsible for the general organ blood supply.
It is worth noting that the liver itself produces the bile, which is eventually stored in the bile canaculi. When many bile canaliculi come together, they end up forming the bile ducts. When bile has been produced, it can either be stored temporarily in the gall bladder or it can be drained directly to the duodenum (Worman 16).
To reduce friction that might be brought by other organs the liver is covered by visceral peritoneum. The hilum defines the area that the veins and the common bile duct enter. Most functions that the liver is supposed to execute are carried out by the liver cells. No organ has come up to emulate these functions although there is an artificial alternative called liver dialysis that seems to be the treatment of liver failure.
This organ plays the function of synthesis, break down and other functions. It is responsible for amino acid synthesis, carbohydrates and protein metabolism as well as deregulation. Arguably the liver acts as the main site where red blood production takes place (for fetus) and also enhances coagulation factors (prothrombin, antithrombin, fibrinogen and proteins).
Emulsification of fats is possible because of the bile that the liver excretes and produces. It also produces a growth factor that looks like insulin which is very vital in the growth of children with a continued anabolic effect in adults. Thrombopoietin production has a good site in the liver and this is a hormone that regulates the way platelets are produced by the bone marrow (Lyratzopoulos 24).
Through drub metabolism the liver is always able to break down medicinal products and toxic substances. Ammonia in our bodies can be very toxic and the liver comes in handy to convert it into urea. Break down of insulin and hemoglobin is done in the liver. The liver also stores glucose that has been converted from glycogen.
Albumin which is a major component of blood comes from the liver. It is undeniable that the liver supports many organs in our body and is essential for survival but this strategic importance has exposed it to a lot of diseases. This paper will mostly look at liver failure its causes and how the society has approached it.
Discussion
There are many diseases that affect the liver or come about because of its functions. They might include infections like Hepatitis A, B, C, and E, Fatty liver, cancer, drug damage, cirrhosis and alcohol damage. Increased levels of bilirubin accompanied by jaundice have been the cause of major diseases (Lyratzopoulos 26).
The liver is also exposed to many pediatric diseases, namely; alagille syndrome, langerhans cell histiocytosis, biliary atresia etc. On the other hand the liver has a great capacity to regenerate and these diseases are only manifested after a great damage. Blood tests can be used to diagnose the liver diseases in advance. To show the extent of the damage live function testing can be employed. In cases where it has been suspected to be an infection then other sociological tests are used.
When the cause of the problem is not known then a biopsy is used to look at the damage done to the liver. The liver has the capability of regenerating into another one because its tissue can regenerate.
Liver failure is the inability of the organ to perform its normal functions as part of the expected physiology (Worman 27). There are two forms of liver failure namely; acute liver failure and chronic liver failure. Acute liver failure is said to be the case where hepatic encephalopathy develops and proteins are produced at a low level within the first month of a liver problem. It is further divided into hyperacute and subacute liver failure.
Chronic liver failure on the other hand is manifested through cirrhosis.

Cirrhosis is brought about by many causes like Hepatitis C or B, metabolic causes, autoimmune hereditary and excessive alcohol intake. Acute failure is very uncommon as it affects the mental status of an otherwise healthy individual. In cases of liver failure there have been severe complications including; encephalopathy, cerebral edema, renal failure, coagulopathy and unexpected death. Acute liver failure can be treated if detected early and its effects reduced as it is usually an overdose of acetaminophen (Palmer 25).
There are many symptoms of liver failure but they depend on what is causing the failure. The most visible sign of its occurrence is discoloration observed in the mucous membrane and parts of the skin. A brain disorder is also another symptom which occurs as waste products accumulate in the blood because the liver cannot adequately filter well.
Liver failure can also be seen when an individual has drowsiness (feeling a sensation of tiredness, sleepiness, lethargy, exhaustion or weariness). In addition to this, restlessness can also be used as a symptom. As a result there are many complications that are always associated with liver failure. They include brain disorders and death of the patient in question. These complications can be said to be secondary symptoms and conditions that arise out of failure of the liver (Palmer 5).
It is very hard to diagnose liver failure and many approaches have been put in place;
- When a viral hepatitis is suspected then it is good to order a hepatitis profile.
- Pressure test are supposed to be done in cases where there is congestive heart failure.
- The various forms of cirrhosis can be tested using liver biopsy.
- For infectious diseases it is good to use skin tests and antibody titers.
There are also items that can be very important in the diagnosis; a blood test can be an alternative to biopsy, obesity leads to liver diseases and that people who receive blood transfusion can also get liver problems (Shariff 22).
As a medical problem liver failure needs to be treated so as to avoid deaths. It is always advisable to seek professional advice in cases where treatment is needed. The first step towards the treatment of liver failure is to understand the underlying cause of the problem. In treatment one can either use; intensive care, treatment of the underlying causes and a liver transplant. A home remedy that may be helpful in liver failure treatment is Neominophagen C (Shariff 29). The only widely used and acceptable therapy to liver failure is transplantation though there are shortages in donor organs
In some cases liver transplant has been widely used to solve the problem of liver failure. The first case of transplantation was done in the United States by Thomas Starzl (Shariff 24). There are two systems used in liver transplants (non-cell based system and non-biologic support system).This is an option for those patients with irreversible liver failure in cases revolving around cirrhosis (alcoholism, hepatitis etc) and many others. Transplantation is also done for fulminant hepatic failure where it mostly occurs within days.
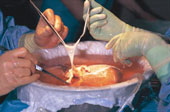
The liver to be used for the transplants is mostly sourced from non- living donors but there is also living donor transplantation. In cases involving living donors a portion of the liver is removed to replace the entire liver of the person to receive it. In recent cases it has been easy to carry out adult to adult liver transplants. The ability of the liver to regenerate has enabled people involved in the transplant to go on smoothly with their lives so long as it is successful (Palmer 18).
With more research there are latest treatments to liver failure like; Nasogastic suction, Isotonic IV fluid, ERCP papillotomy, and balloon or basket retrieval. In recent years nonalcoholic steatohepatis and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease have been common and they are termed to be very risky. To enhance the lives of those with liver failure there is need to establish an artificial liver support system. People are supposed to change their lifestyles as most of the new trends to life have significantly contributed to increased cases of liver failure (Palmer 14).
Conclusion
It should be noted that the liver is the main producer of bile which is later stored. No organ has come up to emulate the functions of the liver although there is an artificial alternative called liver dialysis that seems to be the treatment of liver failure.
Toxic substances and majority of the medicinal products are easily broken down by drug metabolism. In addition to these, it is also able to convert ammonia in our bodies into urea. Break down of insulin and hemoglobin is also done in the liver. It is undeniable that the liver supports many organs in our body and is essential for survival but this strategic importance has exposed it to a lot of diseases.
On the other hand, the liver possesses some properties that enhances its regeneration thereby majority of the diseases are only manifested after extensive damage occurs to the liver. Liver failure is the inability of the organ to perform its normal functions as part of the expected physiology. There are many symptoms of liver failure but they depend on what is causing the failure.
As a medical problem liver failure needs to be treated so as to avoid deaths. It is always advisable to seek professional advice in cases where treatment is needed. The first step towards the treatment of liver failure is to understand the underlying cause of the problem.
Works cited
Fotosearch. Liver disease illustrations and clipart, 2010. Web.
Fotosearch. Liver transplant stock photos and images, 2010. Web.
Lyratzopoulos, Georgios., Tyrrell, Claire., Smith, Paul, and Yelloly, Julia. Recent trends in liver resection surgery activity and population utilization rates in English regions. Cambridge, UK: University of Cambridge, 2007. Print.
Palmer, Melissa. Hepatitis and liver disease: What you need to know. New York: Penguin Group, 2004. Print.
Science Daily. Findings could help diagnose and treat liver cancer, 2010. Web.
Shariff, Mohammed. Current Trends in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Obesity & Diabetes Mellitus. London: Imperial College London, 2009. Print.
Worman, Howard. The liver Disorders. U.S.A: Chicago, 1999. Print.

