Introduction
Health care services have greatly changed over the last decade due to inflation, an increase in population, and advances in technology. This means the Health care system has a challenge of embracing inevitable technological transformations for the provision of quality services. The invention of advanced medical equipment has enhanced effective diagnosis thus offering appropriate treatment leading to increased life expectancy. This permits a satisfactory quality of life, even to individuals with one or more chronic illnesses. Another challenge is the increase in population which has increased the demands for more services thereby causing escalation costs. Apart from those, Inflation is another issue that has led to escalating health care costs (Getzen, 2007).
Health care and economics
Economics affects various sectors including manufacturing of finished products, roadways, railways, air transport, postal services, food distribution system, etc. However, the most detrimental impact of economics is witnessed in the hospitals and the health centers as evidenced by inadequate funds for medical interventions and other life-support systems for saving lives of the underprivileged (Gotten, 2007).
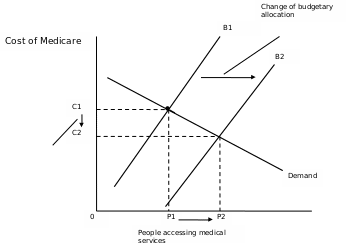
Fiscal policies as a branch of economics, also contribute to the challenge by misallocating funds that are meant for health care, thus affecting the quality of service offered to the population. The graph below shows the effects of the government’s action through fiscal policy on health care. It is evident that when the budgetary allocation is increased, the cost of accessing medical care decreases thus increasing the number of people accessing medical services (Jain and Hanna, 2009).
- Quality – To ensure that the entire nation is working more efficiently and productively, then the healthcare system must be sound and proficient. This involves the organization of institutions, people, and resources in a way that they will provide health services that satisfy the health needs of the entire population. Individual perceptions may deter the provision of quality of services as well as interfere with the interpretation of quality of life procedures that may be of benefit to the nation. Scholars posit that the perceptions of the healthcare service provider may also affect the quality of care. This may lead to burnout and ultimately impede the care given and recommendations made to patients. Clear objective decisions must be taken to ensure patients improve their quality of life substantially (Graban, 2008).
Several things can be done to improve health care services. It entails a multidisciplinary approach by managing symptoms. In cases of chronic problems, patients must be treated and carefully assessed to prevent any other opportunistic diseases and help them deal with the pain and stress. In addition, proper nutritional care and exercising are also important remedies (Graban, 2008).
Within the healthcare team, nurses are typically at the center of communication and are relied upon to facilitate crucial transitions in patient care. Proper communication skills should be embraced by nurses/doctors especially when communicating among themselves or with patients and caretakers. For instance, techniques for the effective use of communication skills may be vastly improved through the use of briefings and cultivating suitable assertiveness within teams as well as team-building activities.
- Technology – Various technological advances have made the world’s industries include the healthcare industry to grow very fast. With the proper use of technology, health care services will improve dramatically—time and effort will be saved and potential errors will be reduced. Above all, keeping up with technology can help health care service providers attain goals of high quality of service and better health results (Gossink and Souquet, 2006 p 1-13).
Considering the increasing demand for health care services as well as technological advances, healthcare service providers must fully understand the system in which they operate to improve the quality of services. This means that there is a need to re-evaluate data pertaining to the current demand for the services, the capacity of current medical technology, and the skills and knowledge of the people operating the machines and required changes (Gossink and Souquet, 2006 p 8).
- Costs- healthcare costs are on an increasing trend due to an increase in cases of chronic conditions such HIV and AIDS, and other non-communicable diseases such as obesity and the aging population. The healthcare costs of the elderly are found to be on the higher side as compared to that of young people. While some people favor rationing of the healthcare services for the elderly to bring down healthcare costs, others think age-based rationing is not an appropriate option for reducing healthcare costs. Through healthcare reforms that encourage functional independence and more community-based care for the elderly, it is possible to bring down the costs of healthcare for the elderly (United Health Group, 2010).
The aging population is not a sudden event but gradual thus the cost of healthcare might be based on personal experience and people will tend to believe that their costs are higher as they grow old. Further, the increasing costs of healthcare can also be attributed to recent developments in medicine. The key to reducing healthcare costs would be to limit expensive drugs and treatments with marginal benefits. Another argument is that healthcare costs are increasing mainly because prices are now fixed by the private healthcare industry with the support of the government. The government should offer subsidies to reduce the cost. Moreover, aging alone cannot be the only factor driving the rising cost of health care. Inflation raises the cost as well. Inflation arises due to the cost of new drugs, technology, and procedures, an implication that the healthcare cost will remain high so long as there is inflation (United Health Group, 2010).
To solve the problem of increasing healthcare costs, some people who have found the services to be unreasonably high, suggested the method of rationing. Rationing refers to the process by which medical care is subjected to limitations due to a shortage of money and in a non-discriminatory fashion. However, there is a debate regarding the issue of discrimination. To halt the rise in medical expenditures a logical measure has to be implemented to identify a group that needs the funds for healthcare – as there is an increase in size and demand (United Health Group, 2010).
Conclusion
Health care services are enmeshed in a crisscross of variables; inflation and budgetary allocation. This takes us to the issue of considering the payoff between quality health care for the general civilian masses and a marginal section of low-income earners. One must remember that an improved economy will ultimately trickle down to all people, thereby increasing access to healthcare.
References
- Getzen, T. E. (2007). Health economics and financing. Hoboken NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
- Gossink, R. & Souquet, J. (2006). Advances and trends in healthcare technology. In, G. Spekowius & T. Wendler (Eds.), Advances in healthcare technology: Shaping the future of medical care (1-13). Dordrecht: Springer.
- Graban, M. (2008). Lean Hospitals: Improving Quality, Patient Safety, and Employee Satisfaction. New York: Productivity Press.
- Jain, T.R. & Hanna, O.P. (2009). Basic Economics. New Delhi: F.K. Publications.
- United Health Group. (March 2010). Why are Health Care costs rising?

