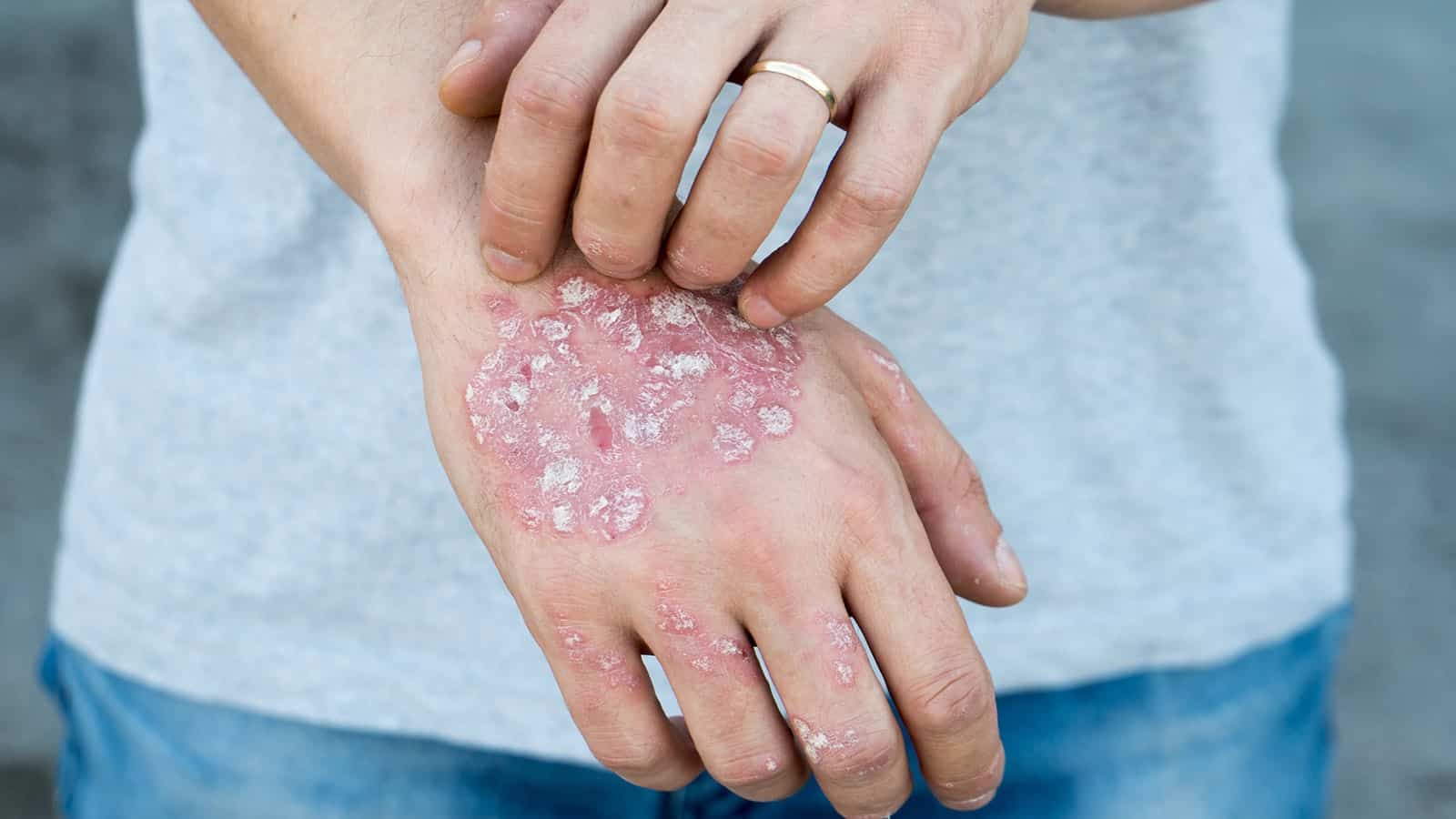
Atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema, is an inflammatory chronic skin condition that is usually diagnosed among smaller children. It appears in the form of inflamed skin followed by severe irritation that causes itchiness. The specific cause of dermatitis remains undiscovered but is thought to be due to a “leaky” skin barrier, which makes skin extremely dry due to the leak of the body’s water. Leaky skin can be caused by genes inherited from parents or by factors in the environment (“Eczema Atopic Dermatitis: AAAAI”).
Symptoms of eczema can vary from one person to another, depending on their age. Common symptoms occur in the form of dark dry skin patches, and possible inflammations, redness, and itchiness. Atopic dermatitis commonly develops in infants and toddlers, however, with age, it disappears in most cases. Atopic dermatitis is not contagious, therefore one cannot get infected by it from another individual. The lesions where eczema usually appears are arms or legs, but with ineffective treatment, it may spread to the torso and hands. In most cases, the wounds of atopic dermatitis are grouped.
A doctor can diagnose atopic dermatitis by assessing the physical condition of a patient’s skin. However, as part of a patient’s exam, a physician should also review their medical history, to know whether an individual has any allergies or asthma. A doctor may order blood and skin patch tests to rule out other conditions of the illness (Staff, 2017).
At the moment, there are a few different treatment methods for atopic dermatitis. They include topical therapies, ointments, creams, a mix of oil and water, solutions, and lotions (“Eczema Atopic Dermatitis: AAAAI”). Because the cause of atopic dermatitis remains unknown, it is impossible to find the methods of its prevention or the cure to this disease. However, eczema can be managed by proper treatment and avoidance of the things that trigger it (Staff, 2017).
Living with atopic dermatitis may be challenging; however, with proper treatment and diet, the symptoms of this disease can be reduced to the minimum; therefore, one can avoid any complications.
References
Eczema Atopic Dermatitis: AAAAI. (n.d.). Web.
Staff, F. E. (2017). Eczema and Atopic Dermatitis. Web.
Appendix
A picture of a person with Atopic Dermatitis.