Breast cancer has become a major health issue in modern society, especially among African American women. The major causes of breast cancer among the group mentioned above are poor nutrition, socioeconomic problems, and lack of sporting activities. The issue of breast cancer ought to be addressed appropriately in order to mitigate its effects on minority groups. Most Black women do not have formal employment or reliable businesses because of racism and discrimination. As a result, their financial abilities do not allow them to seek quality medical services from the various healthcare facilities. Healthcare professionals are tasked with ensuring that appropriate measures to curb breast cancer among Black women are implemented. There are several strategies that healthcare professionals can utilize to ensure early detection of breast cancer so that appropriate treatment can be initiated. An overview of the relevant literature has shown that there is a clear correlation between dietary and lifestyle choices and breast cancer risks in African American women.
The Effects of Nutrition and Lifestyle on Breast Cancer Development in Black Women
Despite the efforts to curb the rates of breast cancer development in women, the disease in question continues to affect women’s life expectancy, health, and overall quality of life. The significance of many crucial elements in the regular biological operation of organ systems in a particular population is the main focus of the integrated review. Specifically, the paper aims to determine the effects of nutrition and lifestyle on breast cancer development in Black women. These days, a significant issue is the correlation between the likelihood of leading a healthy lifestyle and comparatively poor or uncertain socioeconomic status. Some families cannot provide the essential nutritional components in their meal plans, along with busy schedules and minimal sports activities implemented. In the end, such routines can significantly impact a person’s health, including developing serious conditions such as cancer. As a result, the paper will unavoidably discuss aspects other than those that are biologically and medically significant. The reason for selecting the topic in question concerns the vulnerability of the target population. Since the African American community is heavily affected by racism, and its female members’ rights are also infringed upon due to misogyny, African American women have substantially restricted access to healthcare opportunities, particularly in regard to patient education and early identification of breast cancer (Bandera et al., 2021). Additionally, due to racial biases in American society, the nature of breast cancer in African American women is underresearched (Bandera et al., 2021). Therefore, studying the factors such as nutrition and lifestyle choices on the development of breast cancer in Black women will foster improvements in the quality of care.
The objectives of the paper include selecting the relevant studies for further review, identifying the core nutrition- and lifestyle-associated factors that are believed to affect the propensity toward developing breast cancer in the target population, and proposing appropriate changes to the dietary and lifestyle habits of African American women to avoid the development of breast cancer.
Research Question
With consideration of the mentioned variables and target population, the research question can be formulated: what is the effect of nutrition and lifestyle maintained on breast cancer development in Black women?
Research Hypotheses
- Poor nutrition is a major cause of breast cancer among Black women in the United States.
- The majority of Black women live in poverty, which raises their risk of breast cancer, as a result of their precarious socioeconomic status.
Research Variables
- Dependent variable: Prevalence of cancer cases among Black women
- Independent variable: role of healthcare professionals and healthcare facilities
Background
There have been numerous breast cancer cases among Black women, and the main causes have been linked to poor nutrition and lifestyle. Healthcare professionals have also failed to implement effective strategies to address the issue of breast cancer, thus, leading to its prevalence. Such failures not only dent facilities’ public images but also substantially reduce patient confidence and generally affect the performance of healthcare professionals and facilities. Studying the topic herein is crucial for several reasons. First, healthcare administrators should be guided on how to approach the issue of breast cancer among Black women by educating them. Secondly, healthcare professionals and administrators should be equipped with appropriate skills and knowledge to educate the affected population on how to improve their nutrition and lifestyle to avert the issue of breast cancer. Thirdly, the government has a major role to play in addressing the issue of breast cancer by ensuring that all citizens in the country have access to quality medical care, regardless of their socioeconomic positions. Therefore, the integrated reviews aim at identifying the reasons behind the prevalence of breast cancer among Black women and the strategies that should be implemented to promote good health among the target population.
Literature Search
Keywords and Combinations
The search for relevant sources for this integrated review relied on search terms that identified appropriate sources with relevant information. The first keyword combination used in the search process was “breast cancer among Black women.” This keyword combination led to the identification of numerous sources detailing the issue of breast cancer among Black women in the United States and other countries worldwide. Due to the lack of further specifications on the required sources, the search led to the identification of sources dating back to the mid-20th century. The search also identified sources that explored other cancer types prevalent among women globally. The other keyword combination used in the search process was “the effect of nutrition and lifestyle on breast cancer” (Iacoviello et al., 2021). This keyword combination also identified numerous sources detailing how nutrition and lifestyle can lead to increased breast cancer cases among women.
Notably, the keywords mentioned above were used with slight variations in order to improve the search outcome. Specifically, articles, conjunctions, and prepositions, including “the,” “among,” “of,” “and,” “on,” and similar elements, were eventually removed from the search, which allowed obtaining much more accurate results. Furthermore, the initial use of “African American” was finally replaced with “Black” to shorten the keyword combination. For this reason, the following keywords turned out to be the most effective in eliciting eh required search results: “breast cancer Black women” and “nutrition lifestyle effects breast cancer.” Operators such as “AND” were eventually omitted to keep the keywords shorter, which contributed to improved search results.
Some sources explored the issue of nutrition alone, and others explored the issue of lifestyle alone. Besides, other sources combine the two issues, nutrition, and lifestyle, and establish how they contribute to the rise of cancer cases, especially among African American women. The other keyword that was utilized in the search process was “breast cancer.” This search term led to the identification of many sources (Iacoviello et al., 2021). Most of the sources identified discussed the causes of breast cancer, others discussed the effects of breast cancer, and others discussed the ways to mitigate the prevalence of breast cancer among women.
Databases Used
There are numerous databases where sources containing nursing and healthcare information can be found. However, not all nursing databases provide reliable patient data confidentiality information. The sources for this research project were obtained mainly from three databases. The first database to obtain reliable sources for the research project was CINAHL. CINAHL has been approved as a reliable nursing database because it provides over seven million sources with relevant information concerning healthcare provision (Dehghan Salmasi et al., 2021). CINAHL also provides sources with current information that healthcare professionals can use to solve contemporary issues in the healthcare sector. The other databases used to obtain research project sources were PubMed and Nursing Reference Center. These databases provide millions of sources detailing relevant information about the various sectors in the healthcare system. The databases contain reliable sources to guide healthcare professionals in raising awareness among Black women on the prevalence of breast cancer and the most appropriate ways to deal with it. The various databases used also provided specific sources that explored breast cancer among Black women, thus, enabling the researchers to gather relevant information and answers to the research question.
The reliability of the databases in question was assessed by considering some of the core characteristics of the specified repositories of academic articles. Namely, academic databases such as CINAHL, PubMed, and the Nursing Reference Center, are characterized by high levels of data integrity, which implies that the information provided in the databases is consistent throughout the academic repository and highly accurate. Another important aspect of the specified databases concerns the great extent of data safety, particularly data protection against unauthorized changes and the introduction of deliberately misleading or erroneous information. Consequently, the specified databases contain only verified and factually correct information that can be used for research. Finally, the fact that data can be easily recovered in academic databases such as CINSHL. PubMed, and the Nursing Reference Center, suggest that essential information concerning a specific issue will remain in place and readily available to be used for further studies. When combined, the specified characteristics of the databases selected for this project are highly reliable, which served as the key reason for choosing them for this project.
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
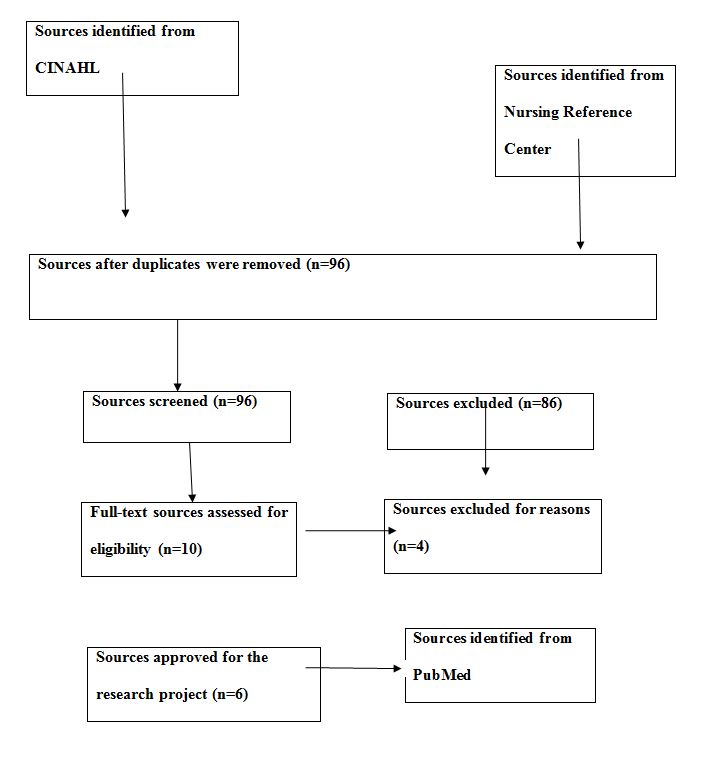
The identified sources from the three databases were filtered to ensure only the most relevant sources were obtained. The sources were narrowed down to include sources published in the last five years that contained information about the United States healthcare system. The sources were also filtered to include only the sources that explored the prevalence of breast cancer among Black women. Sources that explored the prevalence of breast cancer among women, in general, were excluded from the search process. Sources containing statistics about breast cancer among Black women from other countries were also excluded because they did not meet the criteria utilized in the search for the research sources. The sources identified were also narrowed down to include only peer-reviewed sources and from reliable databases. The inclusion and exclusion process is presented below using a flow chart method, as shown in Figure 1. The decision to narrow down the search was defined by the need to focus specifically on the needs of African American women and consider only the studies that dealt with the issues of dietary and lifestyle changes. Thus, the final sample was determined based on its relevance, publication date, and the research type, namely, the use of primary research.
Methodology
Researchers can utilize various methodologies to collect data needed for a research study. Secondary data analysis was the most reliable data collection methodology for this research activity. Secondary data analysis has become influential in research activities because it provides the researchers with recorded data that can help them conduct their analysis and identify reliable answers to the research questions (Ruggiano & Perry, 2019). In secondary data analysis, the researchers rely on documented information that can be obtained from the internet, libraries, or other sites that have reliable information concerning various issues in the field of research and healthcare systems. This research activity relied on data obtained from published sources, which were mostly obtained from the internet. All the sources used were peer-reviewed and published within the last five years. The sources effectively answered the research question on the effects of nutrition and lifestyle maintained on breast cancer development in Black women.
In this research, the qualitative methodology was used to determine the core factors associated with the lifestyle and dietary habits of African American women in relation to the threat of them developing breast cancer. Specifically, the systemic review method was utilized to conduct the necessary data, whereas the collected information was evaluated with the help of textual analysis. The specified solution was quite effective for answering the research question and proving the initial hypothesis concerning the importance of dietary choices and lifestyles on the tendency to develop breast cancer in African American women. Namely, the proposed solution has led to the identification of crucial factors associated with food choices and the extent of physical activity in the target population on the exposure to the threat of breast cancer. The sources provided conclusive information on how nutrition and the lifestyles prevalent among Black women lead to the rise of breast cancer cases among Black women. However, the methodology used needs to be improved by conducting interviews and questionnaires to obtain first-hand information from the Black women affected by breast cancer and the healthcare professionals tasked with caring for Black women diagnosed with breast cancer. Obtaining first-hand information about a health issue helps researchers find more conclusive answers to their research questions because the data obtained is current and explores current issues. That way, the data obtained for the research activity would be more reliable.
However, the methodology can be further improved by introducing quantitative elements into it in order to determine the extent of change that the choice of a particular diet or lifestyle has on the level of risk associated with cancer in the target population. Specifically, a study conducted in the context of a healthcare facility with participants representing the control and experimental groups is highly recommended in order to develop a functional strategy for reducing the threat of breast cancer in African American women. The application of randomized controlled trials has been featured quite heavily in the studies chosen for this review, which indicates that the inclusion of the specified research approach leads to quite positive results. Specifically, a range of articles utilized in this study, such as the article by Shoemaker et al. (2018), incorporated the qualitative analysis into the assessment of the core factors affecting the development of breast cancer in black women. The common soil hypothesis and the validated risk prediction model represent particularly compelling specimens of statistical analysis used in the reviewed articles (Iacoviello et al., 2021; Palmer et al., 2021). However, reviews and phenomenological research have also been integrated into some of the articles.
The statistical analysis method used during the data analysis method was hypothesis testing. Hypothesis testing entails testing whether a certain argument about a certain issue is true or false (Lancaster et al., 2018). Hypothesis testing mainly involves evaluating the reliability of a particular agreed-upon observation or prediction of an issue. The two hypotheses formulated before the research activity commenced were that Poor nutrition is a major cause of breast cancer among Black women in the United States. Consequently, because of their precarious socioeconomic status, the majority of Black women live impoverished lives, which raises their risk of breast cancer.
Although the sources used to gather data for the research activity provided reliable information and answers to the research question, some gaps needed to be addressed to make the information obtained more reliable. The first prevalent gap among the sources utilized was the reliance on nutrition and lifestyle only as the only major causes of breast cancer among Black women. Apart from nutrition and lifestyle, there are other major causes of breast cancer among Black women that need to be addressed. For instance, hereditary factors contribute to a great percentage of breast cancer cases among Black women. The existing gaps can be attributed to the biases associated with the location of the studies, namely, the environments that are not conducive to the development of breast cancer.
Advancement in age is another major cause of breast cancer among Black women in the United States. Therefore, the research should have focused on exploring the causes of breast cancer among Black women to obtain more conclusive results. The sources also focused on Black women, limiting the search criteria. Breast cancer has become prevalent among women of all races. Therefore, breast cancer can be effectively addressed if the matter is approached without any population and race restrictions because all races and populations are affected. The research study was conducted among Black women living in marginalized areas. Therefore, the research activity was limited because only the issues of nutrition and lifestyle are prevalent in the marginalized areas.
There also existed some inconsistencies among the sources used for the research activity. Although all the sources were published within the last five years, they explored varied issues concerning breast cancer among Black women in the United States. For instance, the article by Bandera et al. (2021) discussed the need to improve the healthcare system’s current status to address the issue of breast cancer among Black women appropriately. The study was more focused on the marginalized groups, which interferes with the data’s reliability and results obtained. Unlike the article by Bandera et al. (2021), the article by Iacoviello et al. (2021) was conclusive about the issue of breast cancer. The article identified the causes of breast cancer among Black women and suggested the possible strategies that can be implemented to address the breast cancer issue. The article by Mahmoud & Tayyem (2020) also identified the causes of breast cancer among Black women and discussed possible solutions to the problem. However, the article in question did not provide conclusive statistics on the prevalence of breast cancer.
The article generalized its conclusions by identifying breast cancer as a major health issue among minority groups. The article by Palmer et al. (2021) also identified major causes of breast cancer among Black women but did not address the issue among other groups and races in the United States. The other two articles by Parada Jr et al. (2019) and Shoemaker et al. (2018) could not provide reliable statistics about breast cancer among Black women because of the years of publications. The sources could be ruled out due to the new developments concerning breast cancer that have emerged in the last two years due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Synthesis and Interpretation
Table 2. Evidence Table
Compare and Contrast
The articles used for the research identify the major causes of breast cancer among Black women. According to Iacoviello et al. (2021), the major causes of breast cancer among Black women are poor living conditions due to financial instability. There is also a general lack of sporting and exercise activity among Black women, which leads to the prevalence of breast cancer among the target population. The article by Mahmoud and Tayyen (2020) also identifies nutrition and lifestyle as the major causes of breast cancer among Black women. Black women face increased racism and discrimination that deter them from acquiring formal employment, thus leading a poor life. However, the articles by Bandera et al. (2021) and Palmer et al. (2021) explore the need to have the healthcare system improved in order to enable it to deal with the prevalence of breast cancer among Black women.
Overall, most of the studies agree in their interpretation of the available data concerning the effects of dietary habits and lifestyle choices on the development of breast cancer in Black women. Specifically, all of the studies confirm the presence of correlation and strong causation between the specified variables. Specifically, Bandera et al. (2021) indicated that weight gain of at least 10% or weight loss of 5% was linked to an increased risk of fatal outcomes in the target population. In turn, the research by Iacoviello et al. (2021) states that 34% of lethal outcomes in cancer could be addressed by managing the phenomenon of socioeconomic disparities. Given the fact that the latter concerns are linked closely to the issue of race, the specified percentage could be extrapolated to embrace the issues faced by African American women. Thus, it could be suggested that socioeconomic factors driving Black women’s choices of lifestyles and diets affect 40% of breast cancer cases, which is significantly larger than the figures offered by Bandera et al. (2021). Thus, the necessity to connect the issue of breast cancer to socioeconomic and sociocultural factors is obvious.
Based on factors that predispose one to breast cancer, age is one of the premium considerations that the articles have explored. The article by Shoemaker et al. (2018) explores the age factor as a cause of breast cancer among Black women. The advancement of the age of Black women increases the prevalence of contracting breast cancer. Parada et al. (2019) explore how people with cancer can survive by suggesting some living styles that can help women diagnosed with breast cancer cope with the situation. Despite exploring various aspects of breast cancer, all the sources present crucial information about breast cancer among Black women.
Ethical Issues
There are several ethical issues prevalent in the research activity. The first ethical issue in the research activity is patients’ rights. Patients’ rights are essential in any research activity related to the healthcare system because they must be protected. The information obtained about the patients must be confidential and not revealed to unauthorized persons. The other ethical issue is patient safety. The researchers must prioritize patient safety during any research activity in the healthcare sector. The other ethical issue is informed consent (Chang et al., 2019). Before the commencement of any research activity in the healthcare system, informed consent from the patients must be obtained first. If the ethical issues are not solved appropriately, they might derail the researchers from attaining their research goals and targets.
Autonomy allows the researcher to do their work without plagiarism because of their moral obligation. With no autonomy, the medical research information would be filled with fake information and plagiarized data which would devalue the authenticity of the information. Non- maleficence is another ethical issue in medical research (Chang et al., 2019). This means that whatever the research is about or the form in which research is done, it should not be in any way causing harm to other people. The research should be moral enough to prevent any harm to the involved people.
Finally, justice should be every researcher’s main ethical issue (Chang et al., 2019). This is the giving of fair judgment and treatment to everyone. When obtaining data from the people, there should be no favors of any kind; instead, the researcher should ensure that all the qualifying candidates can take part in providing the data (Chang et al., 2019). Information obtained should always be valid scientifically and morally to ensure the safety of the people.
It should also be mentioned that some of the ethical issues and concerns encountered by the authors of the studies in question have served as significant limitations for the further analysis of the data. For instance, the necessity to limit the range of the studies to be selected for the analysis by considering only those that were conducted in accordance with the existing ethical considerations have restricted the extent of data that could be utilized for the analysis. Moreover, since the conducted analysis was rooted in the principles of ethics, utilizing the studies that implied certain conflicts of interest was not deemed possible. Unfortunately, the specified decision has also led to rejecting quite a range of studies that could have helped extensively in understanding the phenomenon under analysis.
Most of the studies utilized for this review represent primary research, which implies sufficient credibility and validity of the research results utilized to construct this paper and its analysis. The objectivity of the research results offered by the authors of the studies under analysis can be proven by the broad focus and large samples by which the studies are represented. Moreover, the objectivity of the original research conducted by the authors can be supported by their approach toward the choice of the sample, the research participants, and the approach toward the analysis. Seeking to increase the random nature of the data collection and assessment thereof as far as possible, the authors of the studies made their research sufficiently credible.
However, while the use of original research has been quite helpful for understanding the effects of proper dietary choices and increased physical activity in the target population’s lifestyles, the studies in question could have provided secondary data as well. However, the specified type of information would have been more difficult to incorporate into the analysis of the effects that changes in dietary choices and lifestyle have on Black women in regard to the threat of breast cancer. Namely, the studies could have provided information referring to statistical data collected by credible organizations, thus, proving the plausibility of the use of the proposed solution for African American women.
Thus, using secondary data for this study would have been a feasible option, provided that the data in question represented the necessary statistical information concerning the application of the proposed treatment options. Namely, the integration of secondary data would have allowed building a better understanding of how the inclusion of a proper diet and a change in lifestyle choices helped African American women avoid developing breast cancer. However, for the purposes of this research, utilizing the information obtained from clinical trials and other academic articles that featured statistical analysis was particularly important due to the opportunity to observe a correlation and causation between the specified variables.
Finally, one must also mention the issue of ethical concerns that some of the studies raised. Though the authors of the selected articles should be given full credit for doing their best to avoid ethical conflicts in the data analysis and presentation, some of the research considered for this paper raised some questions concerning its ethics. Namely, the paper by Shoemaker et al. (2018) could be seen as slightly questionable in terms of the ethical outcomes of the analysis due to the choice of the sampling approach, namely, the use of the technique that did not allow for substantial variation in the sample. As a result, the sampling framework could have led to a slight inaccu8racy in the outcomes, which, given the gravity of the subject at hand, could be seen as ethically questionable.
Patterns and Trends and Secondary Data Use
The common trend in the research is that the major causes of breast cancer among Black women include nutrition and lifestyle. The sources also identify the appropriate ways to mitigate breast cancer among the target population. Although secondary data sources answered the research question appropriately, the research would have obtained more reliable results if data had been obtained straight from research participants (Chang et al., 2019). Nevertheless, the research outcomes are valid as they answer the study question.
Findings
According to this research study’s findings, breast cancer among Black women continues to threaten the well-being of the target population. The recommended action plan is to increase the number of resources and facilities that can increase education and awareness of breast cancer (Chang et al., 2019). An increase in the resources will increase the efficiency of the technology used in the hospital setting; hence more people will be reached and educated about ways to overcome breast cancer and live healthier lives.
The government should also give progressive lessons to the health administrators and healthcare professionals to enable them to become resourceful to the target population affected by breast cancer. The persons working in a healthcare facility should be informed of the importance of educating people on the dangers of breast cancer and devise ways to protect themselves from contracting the disease. The trends in the medical facilities show an increased number of unethical activities, which affect the confidentiality of the doctor-patient relationship. This reduces the patient’s trust in the doctor; hence, the patient will not give adequate information to diagnose and manage their diseases (Iacoviello et al., 2021). This research confirms that there is less security of knowledge of the patient in the underdeveloped healthcare facilities and raises the concern of ethical need for the awareness of patient confidentiality in the hospital setting.
Conclusion
Breast cancer has become a prevalent health issue among Black women in the United States. Breast cancer mainly results from poor nutrition and unhealthy lifestyles adopted by the target population due to low income. The sources’ strengths include their years of publications and the information provided. All the sources used were published within the last five years, making them reliable because they explore current issues and statistics concerning breast cancer. However, the sources only targeted Black women in the United States and focused on nutrition and lifestyle as the major causes of breast cancer among Black women.
However, it should be noted that the studies used for the analysis had certain limitations. For instance, the restricted range of opportunities for analyzing the problem on a larger scale due to the small sample size was observed in a range of articles. Similarly, the issue of the scope should be addressed as one of the core limitations observed in the studies under analysis. Specifically, the articles used for the research limited their scope substantially by considering a rather narrow range of populations, which made the process of results extrapolation quite complicated. Overall, the specified issues could be seen as key patterns observed across all studies, while each research incorporated an individual limitation that had to be taken into account when integrating it into the analysis.
Nonetheless, the outcomes of the studies were reliable and valid since they considered the core factors shaping the interactions between the studied variables meticulously. Furthermore, the external validity of the studies in question can be confirmed by considering the moderate generalizability of the research findings. Though the studies represented quite specific target groups, therefore, narrowing down the populations to which the outcomes could be applied. The general effects of the variables under analysis on the well-being of Black women and, specifically, their predisposition to developing breast cancer could be identified comparatively easily. Therefore, the articles in question can be considered reliable and valid.
Finally, the implications of the research can be described as quite profound since they will define the further choice of strategies for preventing breast cancer development in African American women. Although the causes of breast cancer are not yet fully known, poor nutrition choices and lifestyles leading to the development of health complications have proven to be some of the potential factors causing the emergence of breast cancer in African American women. Therefore, the research implications can be considered quite substantial as the basis for the development of prevention strategies for breast cancer in African American women.
Despite being limited to only a certain population and specific causes of breast cancer, the sources identify crucial information that can help healthcare professionals and the government deal with the health issue. For instance, the sources identify that lack of formal employment, racism, and discrimination are the major contributors to the target population’s poor nutrition and living styles.
References
Bandera, E. V., Alfano, C. M., Qin, B., Kang, D. W., Friel, C. P., & Dieli-Conwright, C. M. (2021). Harnessing nutrition and physical activity for breast cancer prevention and control to reduce racial/ethnic cancer health disparities. American Society of Clinical Oncology Educational Book, 41, 62-78.
Chang, V., Cao, Y., Li, T., Shi, Y., & Baudier, P. (2019, May). Smart healthcare and ethical issues. In 1st International Conference on Finance, Economics, Management and IT Business (pp. 53-59). SciTePress.
Dehghan Salmasi, N., Kazerani, M., Shekofteh, M., & Jambarsang, S. (2021). Acceptance of evidence-based nursing databases by educational nurses using Rogers’ model. Journal of Librarianship and Information Science, 53(2), 321-327.
Iacoviello, L., Bonaccio, M., de Gaetano, G., & Donati, M. B. (2021). Epidemiology of breast cancer, a paradigm of the “common soil” hypothesis. In Seminars in cancer biology. Academic Press, 72, 4-10. Web.
Lancaster, G., Iatsenko, D., Pidde, A., Ticcinelli, V., & Stefanovska, A. (2018). Surrogate data for hypothesis testing of physical systems. Physics Reports, 748, 1-60.
Mahmoud, R. I., & Tayyem, R. F. (2020). Dietary and lifestyle factors and breast cancer risk. Current Nutrition & Food Science, 16(3), 251-259. Web.
Palmer, J. R., Zirpoli, G., Bertrand, K. A., Battaglia, T., Bernstein, L., Ambrosone, C. B. & Trinquart, L. (2021). A validated risk prediction model for breast cancer in US Black women. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 39(34), 3866-3877. Web.
Parada Jr, H., Sun, X., Tse, C. K., Olshan, A. F., & Troester, M. A. (2019). Lifestyle patterns and survival following breast cancer in the Carolina Breast Cancer Study. Epidemiology, 30(1), 83. Web.
Ruggiano, N., & Perry, T. E. (2019). Conducting secondary analysis of qualitative data: Should we, can we, and how? Qualitative Social Work, 18(1), 81-97.
Shoemaker, M. L., White, M. C., Wu, M., Weir, H. K., & Romieu, I. (2018). Differences in breast cancer incidence among young women aged 20–49 years by stage and tumor characteristics, age, race, and ethnicity, 2004–2013. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment, 169(3), 595-606. Web.
