Introduction
Transitional nursing could be defined as a set of services used to ensure a safe and accurate transition of patients from one level of health care to another. Hirschman et al. (2015) talk about transitional care as a “nurse-led intervention” (para. 1). This practice is mainly targeted at elderly patients with chronic diseases who need constant supervision and frequently move from one hospital to another. Adequate transitional nursing is of particular value since it helps to minimize the possibility of repeated hospitalization. In its turn, medication management describes services that optimize the use of medications and includes education of patients, evaluation, and reconciliation of the drugs. The problem lies in patients becoming more sensitive to medication errors when the transition of care happens. Thus, the risk of appearance of these mistakes poses a challenge for practical transitional nursing. This research paper investigates the problems with taking medication in the process of care transition. Below, there is also a summary of the mentioned issue as well as the significance of the topic and the objectives of the present paper.
Significance of the Problem to Nursing
Undoubtedly, adequate nursing is impossible without accurate prescription of medicines and patients compliance with prescriptions. DelBoccio et al. (2015) indicate that in some cases, it is rather challenging for a diseased person to understand the medications and control when and how much to take them. Such behavior does not characterize all the patients since some have relatives to help them take medicines properly or are just more responsible in these terms by nature. Nevertheless, it is essential to ensure that the quality of treatment does not decline due to medication discrepancies once a patient moved from a hospital, where he or she always was under the supervision of nurses, to home, where there is no trained specialist to assist. Consequently, medication management’s significance to nursing lies in the fact that problems with drug therapy threaten the health of a patient and roll back the prior treatment.
Purpose of the Research and Research Question
The purpose of the current research paper lies in identifying the most vulnerable to drug error groups of patients. The second goal is to suggest solutions that could help to minimize the potential probability of medication discrepancies during transitional nursing. According to Wheeler et al. (2018), mistakes with medicines in the majority of cases happen “on hospital admission and discharge” (p. 73). It is so because, at these stages, information on necessary pills could be transmitted incorrectly.
The research question of the given paper sounds as follows: Which category of patients requires specific practices in terms of medicine management during transitional nursing? The preliminary answer is that this group includes elderly patients who either have no relatives to take care of them, or often move from one clinic to another or often re-hospitalized. To answer the raised question, the investigator could use qualitative methods of research and analyze the existing literature. In addition, a set of interviews could be conducted with nurses, physicians, and patients of different ages and health conditions. Talking about the possible solutions that could improve medicine management, one could think of the application of modern technologies so that nurses could trace all the prescriptions online. The more comprehensive and in-depth research should be conducted to answer the research question and either confirm or reject the initial hypothesis.
Master’s Essentials that Aligned with the Topic
Talking about master’s essentials that aligned with the topic, one could think of improvement of quality, healthcare technologies, and advanced nursing practice. The first mentioned essential deals with standards and measures related to the quality of medical treatment. The timely implementation of practice that proved to be useful is one of the crucial skills that this essential allows acquiring. Secondly, healthcare technologies, as it has already been mentioned, might be a step towards the improvement of medicine management in transitional nursing. Therefore, it is precious to be aware of existing technological capabilities. Finally, such essential as nursing practice at the master’s level is overall useful to get skills and knowledge in decision making, use of information technologies, and effective communication with other staff members and patients.
Medication Management in Transitional Nursing Sampling and Reliability
Transitional nursing remains a critical issue for the modern healthcare sector. It ensures that patients will benefit from a careful and effective transition from one level of health care to another and enjoy the improved outcomes. However, because of the complexity of some cases and peculiarities of the target audience (mainly elderly patients with chronic diseases who need special medications), there is a need for an enhanced approach to groups that face the highest risk of developing complications or rehospitalization. In this regard, the given project aims to identify the most vulnerable group of patients that require additional help to escape medication discrepancies when they move from one form of health supervision to another. The offered document provides the theoretical background for the discussed issue by reviewing the relevant literature and outlines the methodology that can be used to attain relevant data needed for the improved understanding of the problem.
Literature Review
The existing body of evidence accepts the critically important role of medication management in transition care. The appropriate use of pills is one of the vital factors that guarantee recovery and the improved quality of care (Hirschman et al., 2015). However, DelBoccio et al. (2015) emphasize the fact that medication control becomes challenging for elderly patients with chronic illnesses. Under these conditions, the risk of mistakes and deterioration of outcomes significantly increases (Cole et al., 2019). The researchers also admit the fact that transitional pharmaceutical care programs have limited effectiveness regarding the reduction of unplanned rehospitalizations because of the complex nature of the issue and the lack of understanding related to vulnerable categories of patients (Karapinar-Carkit et al., 2019). For this reason, the effective approaches that can help to improve medicine management during transitional nursing should be designed regarding the peculiarities of clients and their needs.
In this regard, the task to define the groups of patients who need specific practices in terms of medication management acquires the top priority. It is one of the sufficient ways to provide nurses with additional information that might help them to attain better outcomes (Redmond et al., 2018). Researchers view the provision of detailed instructions, online monitoring, the use of specific devices reminding about the need for medication intake, and detailed instructions as the possible solutions to the problem (Wheeler et al., 2018). They should also rest on the detailed information about clients to determine what approach should be selected and how it can be implemented regarding patients’ lifestyles and unique characteristics.
Methodology
The choice of the methods to collect data and analyze the issue comes from the research question:
- Which category of patients requires specific practices in terms of medicine management during transitional nursing?
The utilization of the mixed method, with the use of qualitative and quantitative paradigms, is viewed as the advantageous option to ensure the sufficient data collection and creation of the theoretical framework needed for discussion of the topic and conclusion. The analysis of relevant literature to determine the category of patients who show the highest rehospitalization rates can help to acquire information needed to conclude about the most vulnerable group that needs specific practices for improved medicine management. Additionally, the conducting an interview with nurses and physicians working within the transitional care will be another approach vital for collecting information about the most vulnerable groups, common mistakes, and interventions that can be seen as useful tools to improve outcomes.
Sampling and Tools
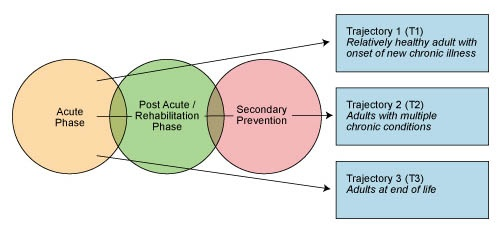
Non-probability, purposive sampling approach will be employed to select participants for the study. The choice can be justified by the fact that it is vital to acquire information from health workers who work within transitional care and possess the experience and knowledge needed for an improved understanding of the problem. For this reason, only specialists with these characteristics should be involved in the research. As for the literature review, it is important to focus on sources related to patients with the experience of transitional care and the use of medications. Interviews can be conducted online by using such tools as Skype, Zoom, or other specific applications. Platforms for surveys can also be used if participants are more comfortable with this mode. The acquired data can be structured and processed by using MS Office standard applications or SPSS analytic tool to investigate information and present in by using graphs. As for the algorithms or flowcharts, the project mainly rests on the paradigm offered previously:
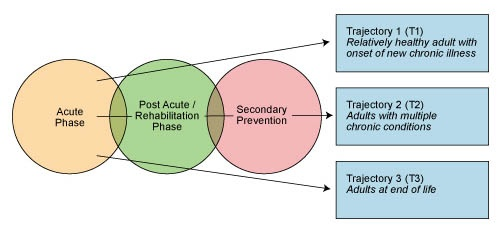
It helps to view the transition care in the appropriate way and work within the given sphere. Additionally, using the acquired data, the graphical representation of the most vulnerable groups by using a segmental diagram can be built.
Implementation
Implementing a research project on the identification of the most vulnerable patient groups who need enhanced medication management strategies in transitional care will require several stages. Given the overall aim of the research, mixed methods will be applied to collect and process data of both qualitative and quantitative nature. According to Shorten and Smith (2017), the utilization of a mixed-method allows for exploring the investigated issue on a more in-depth level. Thus, the research will be carried out by combining the methods of literature review and interviewing with the following analysis of the data by means of software.
Firstly, the initial stage of the research implementation will be a literature review. The recent academic sources will be searched using such scholarly databases as ProQuest, JSTOR, Google Scholar, PubMed, Medline, and others to locate studies published within the past five years in peer-reviewed journals. The inclusion criteria will integrate studies of all designs, which is relevant to the aim of the literature review (Manias et al., 2019). The search will be conducted using such words as ‘transitional nursing,’ ‘vulnerable patients in transitional nursing,’ challenges of medication management in transitional nursing,’ and similar to detect the researches carried out in the investigated field. Upon the completion of the literature search stage, the allocated articles will be screened for compliance with the requirements of addressing the vulnerable patient groups. Ultimately, the identified patient groups will be categorized.
The second stage of the project implementation will involve the creation of interview questions for the participants. At this stage, the qualitative data collected during the literature review will be interpreted by the researcher and used to address the most relevant issues pertaining to the factors contributing to the vulnerability of particular patient groups exposed to transitional nursing. The themes of the frequency of re-hospitalization, the characteristics of chronic illnesses, the barriers to adequate medication intake during the transitional care, and the demographic characteristics of patients will be included when developing the interviews (Hirschman, 2017). Specific categories of patients will be discussed and evaluated as per their vulnerability during the interviews to retrieve the participants’ informed opinions.
The third stage of the implementation phase will be sampling. The participants will be located and contacted by attending the websites of the local hospitals, social media professional groups, and other medical institutions to find specialists involved in transitional care. Physicians and nurses will be non-randomly sampled on the basis of the duration of their work in the sphere and the qualification. Only the individuals who have experience of working in transitional care for five and more years will be sampled for the study. The fourth stage will be the interviewing of the participants. The interviews are planned to be conducted using online video-conferencing platforms Skype and Zoom, as well as telephone communication or face-to-face meetings. The participants will be encouraged to take part in the research with Amazon gift-cards or an alternative incentive.
The fifth stage will require coding the collected data from the literature review and from the interviews. The researcher will recruit assistants to categorize the data concerning the patient groups depending on the level of their vulnerability. Finally, the sixth stage will involve using the SPSS software to run descriptive statistics on the detected categories to identify the most vulnerable population (Knapp, 2016). According to Chiang-Hanisko et al. (2016), the complexity of patients’ conditions, especially in the old age and under the burden of severe chronic illnesses, requires complex approaches in research. Thus, the outlined stages of the implementation stage will address the multifaceted nature of the investigated issue in order to achieve the research goals. Upon the completion of the data processing, the results will be interpreted and discussed. The explicit identification of the vulnerable patient group will allow for providing the evidence base for improving the conditions for this group in transitional care. The needs specific to the group will be a significant contribution to the information available to the transitional nursing staff. Ultimately, the quality of care provided to the patient group will be significantly improved.
The Timeframe for the Project
For the implementation phase to be carried out smoothly and coordinately, a clear plan and a timeframe are required. As shown in Figure 1, the implementation phase consists of six consecutive stages, which will occur immediately one after another and partially based on the completion of the previous step. The duration of one stage will vary between one and four weeks, depending on the volume of work and the requirements of a particular implementation step. Overall, the project implementation will take approximately three and a half months, given that all the processes occur on time without obstacles and delays. It is possible that some difficulties, regardless of the researcher’s efforts, might occur on the stages of participant sampling and recruiting since this process will depend on the contacted facilities and the availability of specialists.
Figure 1. Implementation timeframe
Results
The completed three stages of the project proved that medication management during transitional nursing is one of the essential elements that determine the quality of treatment. In case the medication is not prescribed appropriately, and doctors and nurses do not educate patients about possible side effects, the transition becomes less effective and beneficial for individuals’ well-being. For this reason, it is crucial to identify the most vulnerable to medication management mistakes groups of people and provide solutions that can help minimize the probability of treatment discrepancies during transitional nursing. This project developed all the necessary stages for research fulfillment, such as planning, sampling and reliability, and implementation. Therefore, the following paper will present the study results by conducting a theoretical analysis of various data collected and indicating research limitations and areas for improvement.
Descriptive Data
The participants for the study were chosen the way it was indicated in the implementation phase. The main goal was to conduct interviews from people highly involved in transitional care who understand how the process works in detail and have an experience of at least 5 years. In general, 15 interviews were conducted (6 doctors, 9 nurses) via Skype and Zoom applications. All the study participants worked in the sphere of transitional nursing for more than 7 years and had a chance to treat chronic and elderly patients. The interviewer mainly focused on asking questions about the medical histories of patients and their conditions before, during, and after the procedure of transition. This strategy helped identify medically fragile and socially vulnerable groups of older people who are fundamentally distinct from individuals without chronic problems (Toles et al., 2016). In addition, several questions aimed at receiving a response about intervention characteristics and resources used by medical professionals since these elements are essential while providing transitional care (Toles et al., 2016). The length of all interviews did not exceed 30 minutes, and all the participants signed a non-disclosure agreement.
Results of Statistical Tools
The coding of information collected during the interviews allowed the division of vulnerable patients into various groups according to their health conditions, age, and psychological differences. Assistants recruited by the researchers carefully analyzed the examples of people provided by the study participants and categorized them by taking into consideration their distinguishing features. Coffey et al. (2017) mentioned that elderly people suffer from an increasing level of dependency on others; therefore, assistants created a specific group for such individuals based on the comments of nurses and doctors. Furthermore, adults with severe chronic conditions that do not give them an opportunity to lead a typical lifestyle were placed in another subgroup that needs constant care from relatives or medical specialists (Coffey et al., 2017). Finally, the third group created by the assistants were patients aged 80 and more who do not have chronic conditions and psychological issues but need assistance in buying and taking drugs. These people were put together since, due to their age, they are not knowledgeable and competent enough to make any serious medical decisions.
The SPSS software identified that the most vulnerable group are older adults with chronic illnesses. The program ran the descriptive statistics of all three detected categories in order to define which subgroup experiences the most significant number of challenges when being involved in transitional care. It was concluded that those who have chronic conditions, such as “heart failure, stroke, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cancer, hypertension, and diabetes,” suffer the most from medication management (Son & You, 2015). This result is based on the fact that transitions of chronic patients give significant rise to adverse clinical events leading to individuals having unmet needs and developing a feeling of dissatisfaction with the quality of treatment received (Son & You, 2015). Moreover, if the medication is given to people without considering their individual health problems or side effects, the overall well-being and a particular chronic condition may severely deteriorate (Son & You, 2015). 12 out of 17 study participants indicated that they experience issues when delivering care to chronic patients and choosing the right treatment program. Therefore, this subgroup is the most vulnerable of all three.
The results of this research will help medical professionals to determine the main mistakes that they make during the process of transitional nursing. After analyzing their failures, doctors and nurses will be able to develop appropriate solutions to the existing problems and prevent the emergence of new issues in the future. The overall system of transitional care will be improved, and patients will be more satisfied with the delivered treatment.
Research Limitations
One of the most obvious limitations of this study is that, during the interview, participants provided their subjective opinions about vulnerable groups and ineffective treatment practices. Every professional’s experience is distinct since they work in different environments, use different treatment methods and medications, and help various groups of people and layers of the society. Another possible limitation of the study is that it does not take into account the gender of participants which can also be a critical factor in understanding medication management mistakes. Thus, the study can be improved if patients are divided into more groups and a larger number doctors and nurses are interviewed.
Learning Experiences
This course has provided great insights into the relation between theory and practice in nursing. It has also demonstrated the importance and value of using scientific evidence in decision-making and informing medical policies and guidelines. The experience of designing a scientific study was enlightening and exceptionally informative as to the amount and type of work that goes into discovering or verifying seemingly minute and obvious data. This course has explained why such data that can be easily taken for granted or as self-evident, needs to be evaluated and verified before it can be used to make decisions. It was also a powerful learning experience of going through every step in the study design process. Finally, in the context of transitional care nursing, the course provided valuable knowledge about the evidence-based origins of existing and future policies, and the process of acquiring evidence and applying it to practice. Overall, the instruction and experience received as part of this course will be valuable assets to one’s career in nursing.
Conclusion
Medication management is a vital component of a patient’s health care strategy post-discharge from a hospital. Errors in medication management can have a significant negative effect on a patient’s ultimate outcome (Pérez-Jover, et al., 2018; Kollerup, et al., 2018). Therefore, ensuring that a patient is capable of purchasing and correctly self-administering the required medication or receiving appropriate assistance, if necessary, is a critical part of transitional nursing. To inform further decisions related to preparing patients for discharge and teaching them medication management strategies, a study was conducted to identify the groups of patients who are most prone to errors in medication management.
The present study interviewed health care professionals to discuss patients’ vulnerabilities to medication management errors. Researchers used a combination of qualitative and quantitative methods, including examining patients’ medical history before, during, and after the transition. Interviews were then analyzed and coded for themes identifying groups of vulnerable groups of patients. Three groups were able to be identified. The first group is comprised elderly people, who have an increased level on dependency of others. The second group includes patients with severe chronic conditions that prevent them from leading a typical lifestyle. Elderly patients over 80 years of age who do not have chronic illnesses or psychological issues, but require assistance in purchasing and administering medications comprise the third group. The data was further analyzed with the SPSS analytical tool to highlight the second group, older adults with chronic conditions, as the most vulnerable of the three.
The present study provides insight into patients’ vulnerability to errors in medication management. This information can be used by transitional care nurses in their decision-making process when providing patients with instruction in medication management as part of their preparation to discharge. Furthermore, the knowledge of at-risk patients can help identify patients who need post-discharge intervention, such a follow-up visits or assistive services. However, as the study sampled a limited group of respondents and used primarily qualitative data, its results may be insufficient to inform policy or provide accurate guidelines. As such, further research into the subject is suggested, aimed at finely distinguishing vulnerable patient groups, discover more such groups, or utilize quantitative methods to determine the degree of risk associated with each group. Overall, this research contributes to the field of transitional care nursing by identifying vulnerable groups of patients who may require additional interventions related to medication management.
References
Chiang-Hanisko, L., Newman, D., Dyess, S., Piyakong, D., & Liehr, P. (2016). Guidance for using mixed methods design in nursing practice research. Applied Nursing Research, 31, 1-5.
Cole, J., Moss, M., Fu, D., Carson, P., & Xiong, L. (2019). Impact of pharmacist involvement on telehealth transitional care management (TCM) for high medication risk patients. Pharmacy, 7(4), 158.
Coffey, A., Mulcahy, H., Savage, E., Fitzgerald, S., Bradley, C., Benefield, L., & Leahy‐Warren, P. (2017). Transitional care interventions: Relevance for nursing in the community. Public Health Nursing, 34(5), 454-460. Web.
DelBoccio, S., Smith, D., Hicks, M., Lowe, P., Graves-Rust, J., Volland, J., & Fryda, S. (2015). Successes and challenges in patient care transition programming: One hospital’s journey. OJIN: The Online Journal of Issues in Nursing, 20(3).
Hirschman, K. B., Shaid, E., McCauley, K., Pauly, M. V., & Naylor, M. D. (2015). Continuity of care: The transitional care model. Online Journal of Issues in Nursing, 20(3).
Karapinar-Carkit, F., Borgsteede, S., Janssen, M., Mak, M., Yildrim, N., Siegert, C., Mol, P., Egberts, T., & van den Bemt, P. (2019). The effect of a pharmaceutical transitional care program on rehospitalisations in internal medicine patients: an interrupted-time-series study. BMC Health Services Research, 19, 717.
Knapp, H. (2016). Practical statistics for nursing using SPSS. Sage Publications.
Manias, E., Bucknall, T., Hughes, C., Jorm, C., & Woodward-Kron, R. (2019). Family involvement in managing medications of older patients across transitions of care: a systematic review. BMC Geriatrics, 19(95), 1-21.
Redmond, P., Grimes, T., McDonnell, R., Boland, F., Huges, C., & Fahey, T. (2018). Impact of medication reconciliation for improving transitions of care. Cochrane Database Systemic Review, 2018(8).
Shorten, A., & Smith, J. (2017). Mixed methods research: Expanding the evidence base. Evidence-Based Nursing, 20(3), 74-75.
Son, Y. J., & You, M. (2015). Transitional care for older adults with chronic illnesses as a vulnerable population: Theoretical framework and future directions in nursing. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing, 45(6), 919-927. Web.
Toles, M., Colón-Emeric, C., Asafu-Adjei, J., Moreton, E., & Hanson, L. C. (2016). Transitional care of older adults in skilled nursing facilities: A systematic review. Geriatric Nursing, 37(4), 296-301. Web.
Wheeler, A. J., Scahill, S., Hopcroft, D., & Stapleton, H. (2018). Reducing medication errors at transitions of care is everyone’s business. Australian Prescriber, 41(3), 73-77.
Pérez-Jover, V., Mira, J., Carratala-Munuera, C., Gil-Guillen, V., Basora, J., López-Pineda, A., & Orozco-Beltrán, D. (2018). Inappropriate use of medication by elderly, polymedicated, or multipathological patients with chronic diseases. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(2), 310. Web.
Kollerup, M., Curtis, T., & Laursen, B. S. (2018). Improving visiting nurses’ post-hospital medication management. Journal of Integrated Care, 26(1), 65-76. Web.
