The present DNP project aims at evaluating the effectiveness of a depression detection questionnaire in adults. In order to measure the outcomes of the project, it is possible to utilize the outcome measurement model described in detail by Melnyk and Fineout-Overholt (2019). This framework consists of four phases. During the first phase, it is important to identify the problem and variables, the project’s target and the instruments to be used (see Figure 1). The primary variable will be patients’ diagnoses (the focus is on depression) as the questionnaires are expected to be an effective complementary tool. The target of the project is an effective use of the questionnaires that leads to positive patient outcomes (better diagnostic practices and improved treatment plans). The identification of the required instruments will encompass choosing a database, academic resources, and available communication channels.
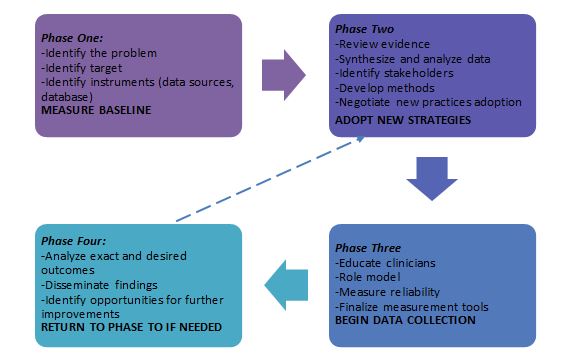
Phase two is associated with the adoption of new strategies, which implies the review of the evidence, the development of methods and guidelines, as well as the establishment of the corresponding teams. The DNP project in question is evidence-based, and the use of the model is well described in the literature. The involvement of interdisciplinary teams where stakeholders understand their roles and have the necessary knowledge, skills, and guidance is critical for any project implementation (Melnyk & Fineout-Overholt, 2019). At this stage, discussions with the stakeholders will play a central role in the process, since it is important to make sure that the clinicians understand the goals, instruments, and expected outcomes. The healthcare professionals will receive the information (synthesized review of the issue and the project, as well as the methodology to be employed) and will be able to discuss the project if necessary.
The third phase is concerned with data collection based on the implementation of the project. Melnyk and Fineout-Overholt (2019) emphasize that being a role model is crucial at this stage as the change agent should properly control the process and guide all stakeholders. It is also necessary to measure the used tools and apparent outcomes, as well as the reliability of the utilized methods. The documentation of all details and paying specific attention to the aspects (and outcomes) that have not been planned is the focus of this step.
The fourth phase is the finalization of the measurement process as the outcomes of the project are analyzed. If necessary, it is possible to return to phase two and go through three phases again. Clearly, certain changes should be implemented and some practices should be shaped in accordance with the received results. It is necessary to identify potential areas for further improvement and specific tools to be employed to address this goal. The dissemination of the data regarding the project is the final activity that requires the delivery of effective presentation and the development of the corresponding protocols or policies. At this stage, the effectiveness of the project becomes apparent: the increase in the number of diagnoses and treatment plans that resulted in positive patient outcomes.
On balance, it is necessary to note that the effectiveness of the DNP project addressing depression detection can be measured with the help of the outcome management model. The analysis of the outcomes will result in the identification of potential areas for improvement or the development of an effective policy regarding the evaluation of patients’ mental health.
References
Melnyk, B. M., & Fineout-Overholt, E. (2019). Evidence-based practice in nursing and healthcare: A guide to best practice (4th ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.

