The issue is the antibiotic resistance in children, and the solution is to cultivate the patient-centered healthcare while highlighting its need with the assistance of a combination of the research, education, and practice. The plan includes stages such as research, increasing awareness about the necessity of the change (education and practice), and cultivating change.
Change Model Overview
The John Hopkins Nursing Evidence-Based Practice Process implies a combination of practice, education, and research while considering internal and external factors to encourage change (Dearholt & Dang, 2012). The model portrays the issue from dissimilar perspectives and ensures the understanding among nurses.
Practice Question
Recruit Interprofessional Team
The monitoring and action team will include a pediatrician, pharmacists, charge nurse, regular nurses, and research analyst.
Develop and Refine the EBP Question
The EBP question can be formulated as ‘Will the patient-centered care and monitoring contribute to the minimization of the negative changes in health conditions occurring due to the antibiotic resistance among children (0-12)?’. The problem is the existence of the adverse effects of antibiotics on the children’s health while the intervention implies the assessment of the treatments and evaluation of the managerial approach, as the patient-centered therapy has to be prioritized due to its potential positive influence on the current problem (Blaser, 2014).
Define the Scope of the EBP
The antibiotics are still regarded as prioritized treatment while their consumption and coverage tend to increase while being an external cause of the necessity of changes (see Figure 1) (CDDEP, 2015).
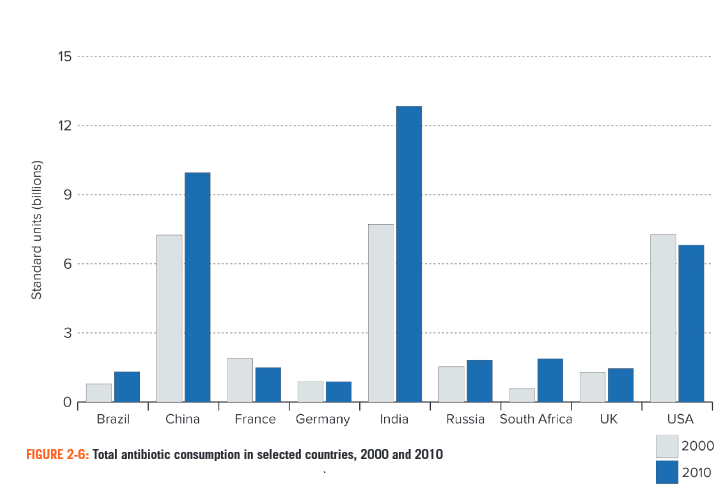
Some antibiotics is a cause Clostridium difficile, as this matter is resistant to the majority of the treatments, and Table 1 depicts its importance in different countries (CDDEP, 2015).
Table 1. Clostridium difficile around the world (CDDEP, 2015).
These external factors depict that the changes are necessary, as they will enhance the prosperity of the population around the world. Meanwhile, the development of a novel internal approach will combine practice, learning, research while improving the patient’s satisfaction and quality of the services and influencing the current medical legislation.
Determine Responsibility of Team Members
The pediatrician and charge nurse ensure the safety of the procedures (education) and determine the compliance with the current legislation. The pharmacists will depict the connection between the theoretical framework with practices and determine the interdependence between the treatments. The regular nurses will be in charge of conducting practical research, and the research analysist interprets the results and ensures the presence of all components of John Hopkins Nursing Evidence-Based Practice Process.
Evidence
Conduct Internal/ External Search for Evidence and Appraisal of Evidence
The selected source covered the issue from dissimilar perspectives while referring to the evidence-based practice and portrayal of potential solutions. In the case, the quantitative researches were utilized to determine the interdependence between variables and emphasize the condition of SDD and SOD during these measures.
Summarize the Evidence
The patient-centered care and individual approach are the matters to improve the health condition of the children with the antibiotic resistance, as the antibiotic resistance is one of the critical concerns and can be diminished by spreading awareness and reducing the animal tests (Assem, 2015; Spellberg, 2013). In turn, the emotional intelligence can enhance the quality of the healthcare (Pitout 2012). Nonetheless, the existent alternatives have to be discovered, as, currently, the usage of antibiotics is one of the most effective treatments while being dangerous simultaneously (Oostdijk, 2013; CDDEP, 2015).
Develop Recommendations for Change Based on Evidence
The primary recommendation is to focus on the patient-centered care, as, despite the analysis of SOD and SDD each client requires a personal approach. The managerial changes have to be introduced while conducting the presence of resistance to the particular treatment individually.
Translation
Action Plan
Table 2. The timeline.
The results will be reported to the leader of the project and will be gathered with the assistance of the surveys while monitoring the positive changes the children’s health condition.
Evaluating Outcomes and Reporting Outcomes
The report will offer a quantitative portrayal of the evidence-based practice and depict the positive changes in the children’s health while decreasing the occurrence of Clostridium difficile in the region by 10% annually. Meanwhile, the patients’ satisfaction inquiry will determine the effectiveness of the change to the customer-centered healthcare.
Identify Next Steps
The program is applicable to the other facilities and can enhance the condition of the children among regions. Nonetheless, it can be utilized at one unit at a time to ensure the efficiency of the proposed change.
Disseminate Findings
The findings will be delivered with the assistance of the reports and publications online. The presence in the popular medical databases will assure the rapid delivery of the message to the audience while depicting a potential solution to the issue.
Conclusion
Based on the factors provided above, the primary issue is related to the children’s resistance to antibiotics while having a negative effect on their health. Meanwhile, the external and internal factors depict that alternative solutions to antibiotics are based on practice, education, and research. The primary resolution is the introduction of customer-centered approach while basing the findings on the research and theoretical background to cultivate the necessity of learning to improve the current condition with the assistance of the practical findings.
References
Assem, H. (2015). Nursing care of infants and children with bronchiolitis. Pediatrics and Neonatal Nursing, 2(1), 43-49.
Blaser, J. (2014). Missing microbes: How the overuse of antibiotics is fueling our modern plagues. Cambridge, MA: Henry Holt and Company.
CDDEP. (2015). The state of the world’s antibiotics 2015. Web.
Dearholt, S., & Dang, D. (2012). John Hopkins nursing evidence-based practice: Models and guidelines. Indianapolis, IN: Sigma Theta Tau International.
Oostdijk, E. (2013). Effects of decontamination of the oropharynx and intestinal tract on antibiotic resistance in ICUs: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Network, 312(14), 1403-1404.
Pitout, J. (2012). Extraintestinal pathogenic escherichia coli: A combination of virulence with antibiotic resistance. Frontiers in Microbiology, 3(9), 1-7.
Spellberg, B. (2013). The future of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance. The New England Journal of Medicine, 368(4), 299-302.

